产品中心Cell Resources
联系我们CONTACT US
 400-999-210024小时服务热线
400-999-210024小时服务热线
产品概述
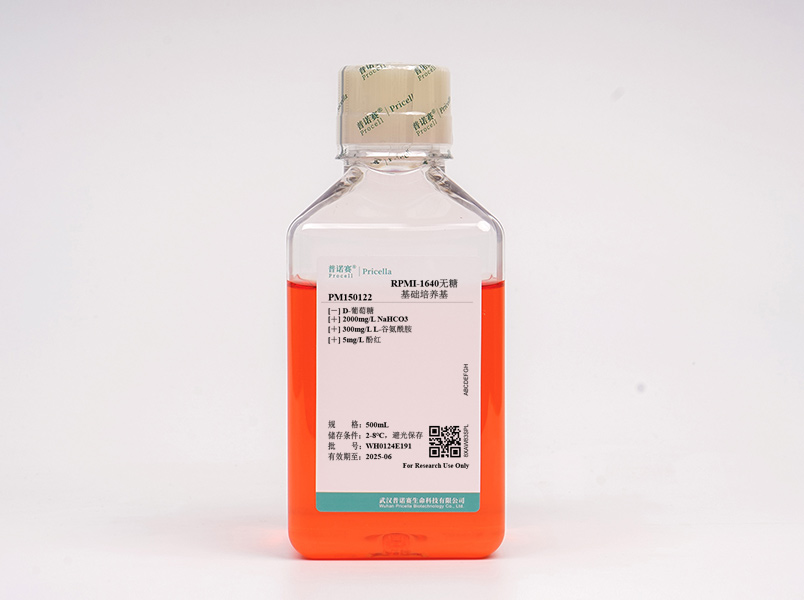
RPMI-1640是Moore等人于1967年在美国纽约州法罗市的罗斯韦尔公园纪念研究所(Roswell Park Memorial Institute, RPMI)开发出来的,RPMI是该研究所开发的一类细胞培养基,1640是培养基代号。RPMI-1640是改进型的McCoy's 5A培养基,使用碳酸氢盐缓冲系统,与大多数哺乳动物细胞培养基不同的是其典型的PH8的配方。RPMI-1640培养基最初是为淋巴细胞培养专门设计的,现在已广泛应用于各种正常细胞和癌细胞的培养,尤其是悬浮细胞的培养,是使用最为广泛的培养基之一。不含葡萄糖的RPMI-1640培养基可以根据研究需要,随意调节葡萄糖的浓度,方便快捷。
本产品含有多类细胞培养所需的氨基酸、维生素、无机盐等多种成分,但不含蛋白质、脂类或任何生长因子,故此产品需搭配血清或无血清添加物使用。
成分说明
形态 | 液体 |
浓度 | 1× |
规格 | 500mL |
pH | 7.2-7.4 |
L-谷氨酰胺 | 2 mM |
NaHCO3 | 2000 mg/L |
D-葡萄糖 | 无 |
HEPES缓冲剂 | 无 |
酚红指示剂 | 5 mg/L |
储存条件 | 2-8℃,避光 |
运输条件 | 常温 |
有效期 | 18个月 |
注意事项
1、本产品经0.1μm过滤除菌,使用时应注意无菌操作,避免污染;
2、为保持本产品的最佳使用效果,请勿进行冻融处理;
3、本产品仅用于科研或进一步研究使用,不用于诊断和治疗。
参考文献
-
High glucose levels promote glycolysis and cholesterol synthesis via ERRα and suppress the autophagy–lysosomal pathway in endometrial cancer (2025-03-17)
期刊:Cell Death & Disease
DOI:10.1038/s41419-025-07499-y
影响因子 :8.1
引用产品: McCoy's 5A无糖 培养基 , RPMI-1640无糖 培养基
-
Enterovirus A71-induced glycolysis is essential for viral replication by activating PI3K/Akt pathway (2025-03-22)
期刊:MICROBIAL PATHOGENESIS
DOI:10.1016/j.micpath.2025.107505
影响因子 :3.3
引用产品: RPMI-1640无糖 培养基 , RPMI-1640 培养基(含葡萄糖)
-
LncRNA TCONS_00067339 as a key regulatory factor inducing decreased cell viability and ferroptosis in neonatal hypoxic-ischemic brain damage (2025-03-08)
期刊:BRAIN RESEARCH
DOI:10.1016/j.brainres.2025.149562
影响因子 :2.7
引用产品: PC-12 (High differentiation) 细胞 , PC-12 (High differentiation)细胞专用培养基 , RPMI-1640无糖 培养基 , RPMI-1640 培养基
-
Novel Combination Therapy for Triple-Negative Breast Cancer based on an Intelligent Hollow Carbon Sphere (2023-04-11)
期刊:Research
影响因子 :11.0
引用产品: RPMI-1640无糖 培养基
-
Glucose restriction induces AMPK-SIRT1-mediated circadian clock gene Per expression and delays NSCLC progression (2023-09-30)
期刊:CANCER LETTERS
DOI:10.1016/j.canlet.2023.216424
影响因子 :9.7
引用产品: RPMI-1640 培养基 , RPMI-1640无糖 培养基
-
1,25-Dihydroxyvitamin D3 Provides Benefits in Vitiligo Based on Modulation of CD8+ T Cell Glycolysis and Function (2023-11-06)
期刊:Nutrients
影响因子 :5.9
引用产品: RPMI-1640无糖 培养基
-
Hyperglycemia Aggravates Periodontitis via Autophagy Impairment and ROS-Inflammasome-Mediated Macrophage Pyroptosis (2023-03-27)
期刊:INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF MOLECULAR SCIENCES
影响因子 :5.6
引用产品: RPMI-1640 培养基 , RPMI-1640无糖 培养基
-
Type 2 diabetes affects arsenic metabolism via transporters in arsenic trioxide treated acute promyelocytic leukemia patients (2023-05-03)
期刊:ENVIRONMENTAL TOXICOLOGY AND PHARMACOLOGY
DOI:10.1016/j.etap.2023.104142
影响因子 :4.3
引用产品: RPMI-1640无糖 培养基
-
PP2Ac knockdown attenuates lipotoxicity‑induced pancreatic β‑cell dysfunction and apoptosis (2023-10-10)
期刊:Experimental and Therapeutic Medicine
影响因子 :2.7
引用产品: RPMI-1640无糖 培养基
-
Oxidized low-density lipoprotein induces M2-type differentiation of macrophages to promote the protracted progression of atherosclerotic inflammation in high-fat diet-fed ApoE -/- mice (2023-12-31)
期刊:CELLULAR AND MOLECULAR BIOLOGY
DOI:10.14715/cmb/2023.69.15.40
影响因子 :1.6
引用产品: RPMI-1640无糖 培养基 , 青霉素-链霉素溶液(双抗),100× , THP-1 细胞 , RPMI-1640 培养基 , 特级胎牛血清
-
Neuroprotective effects of neural stem cells pretreated with neuregulin1β on PC12 cells exposed to oxygen-glucose deprivation/reoxygenation (2022-08-02)
期刊:Neural Regeneration Research
影响因子 :6.1
引用产品: RPMI-1640无糖 培养基
-
Neuroprotective effects of methylcobalamin in cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury through activation of the ERK1/2 signaling pathway (2021-08-12)
期刊:International Immunopharmacology
DOI:10.1016/j.intimp.2021.108040
影响因子 :5.6
引用产品: RPMI-1640无糖 培养基
FAQs
Q:{{item.question}}
A:
产品资料


识别码示意图