产品中心Cell Resources
联系我们CONTACT US
 400-999-210024小时服务热线
400-999-210024小时服务热线
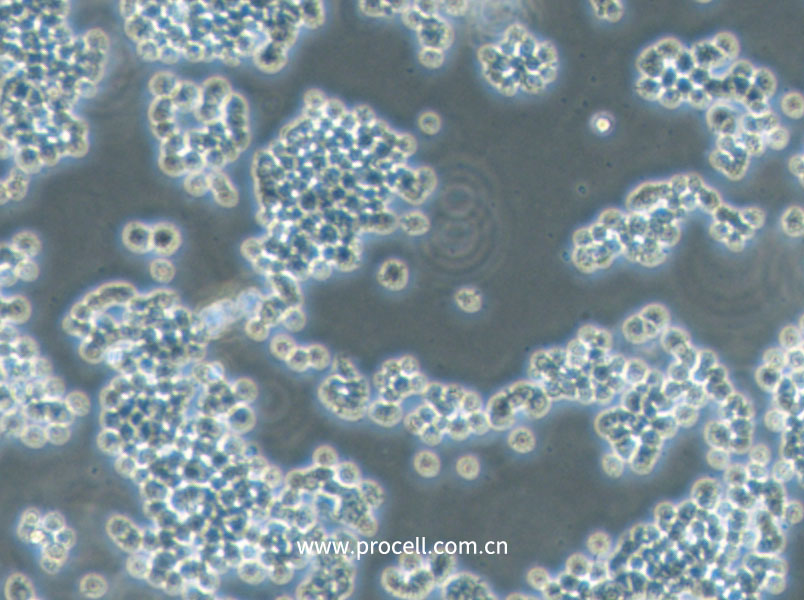
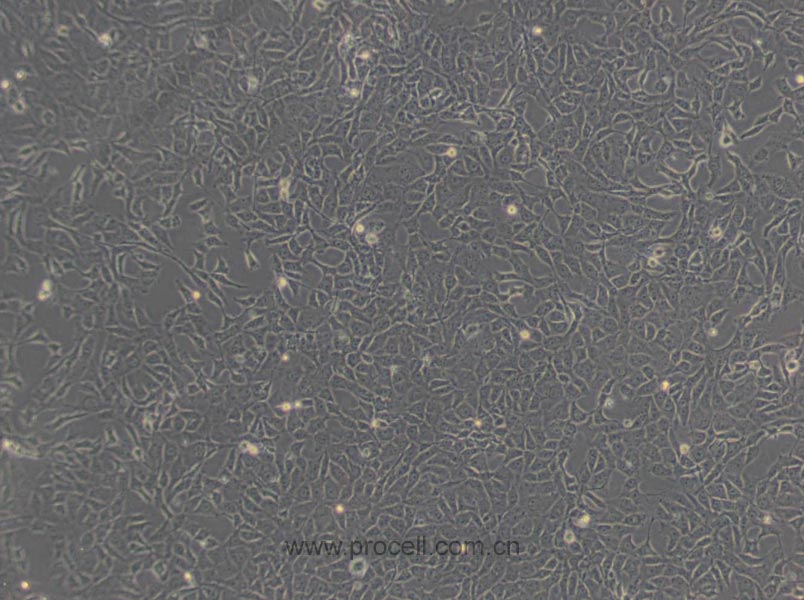
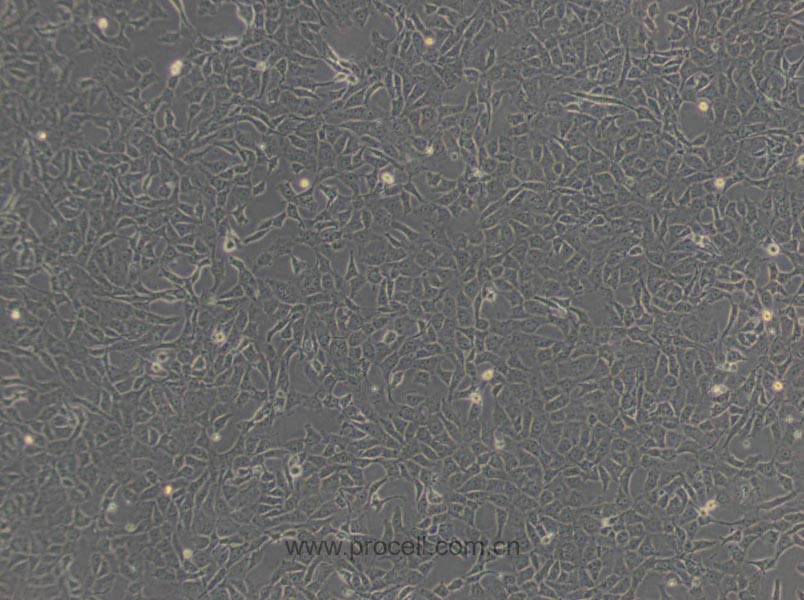
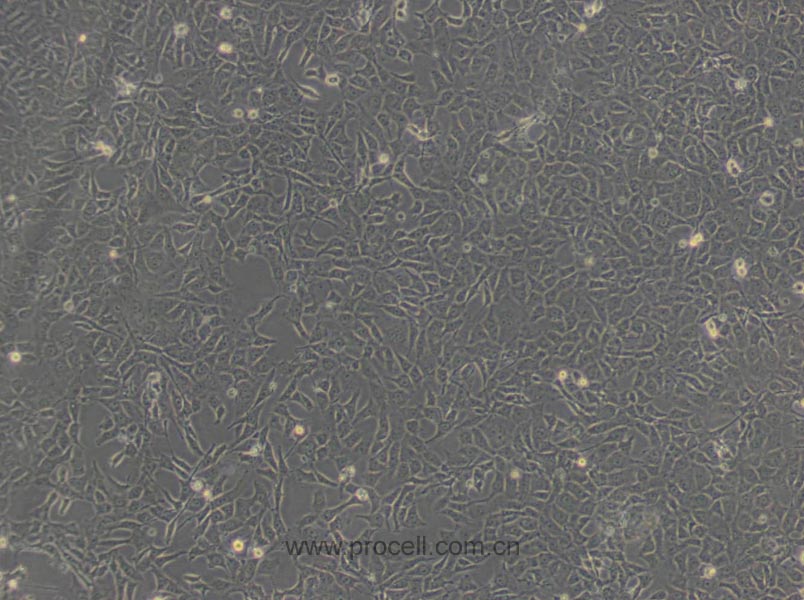
产品概述
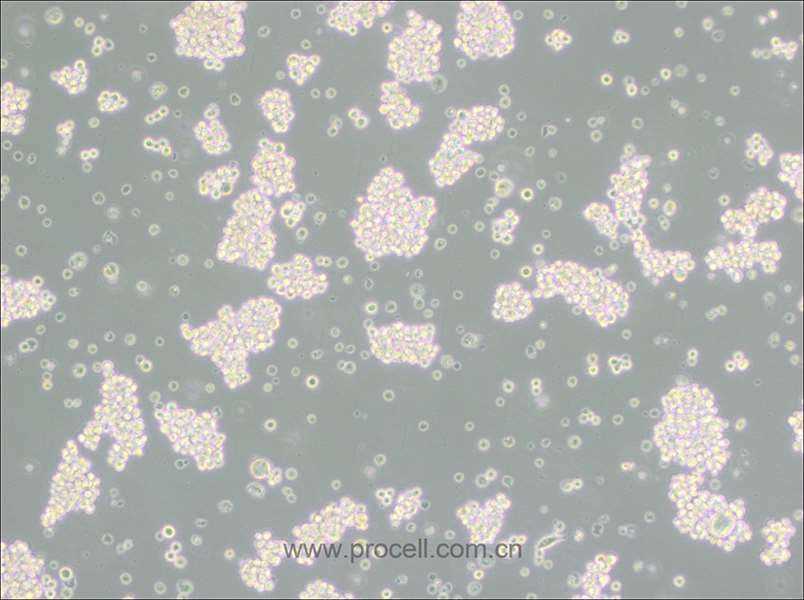
| 名称 | BRL (大鼠肝细胞) (种属鉴定正确) |
| 别称 | Buffalo Rat Liver |
| 种属 | 大鼠 |
| 生长特性 | 贴壁细胞 |
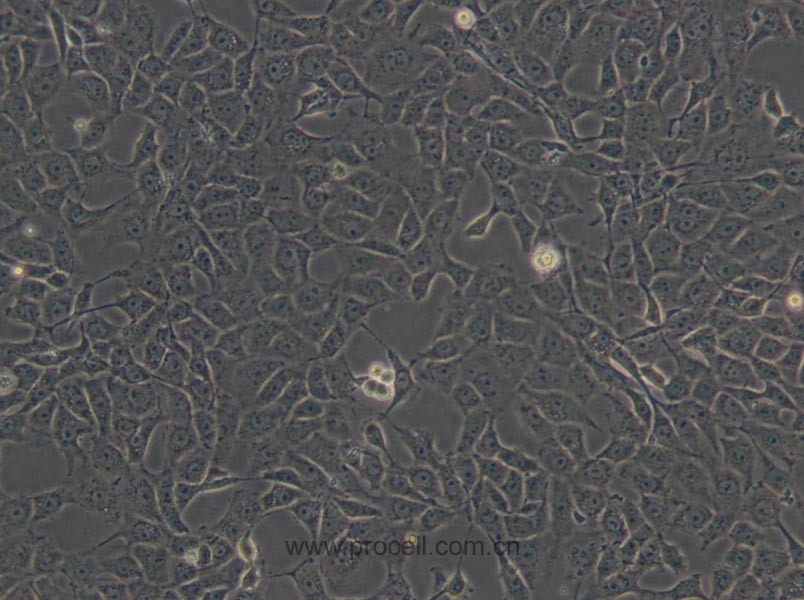
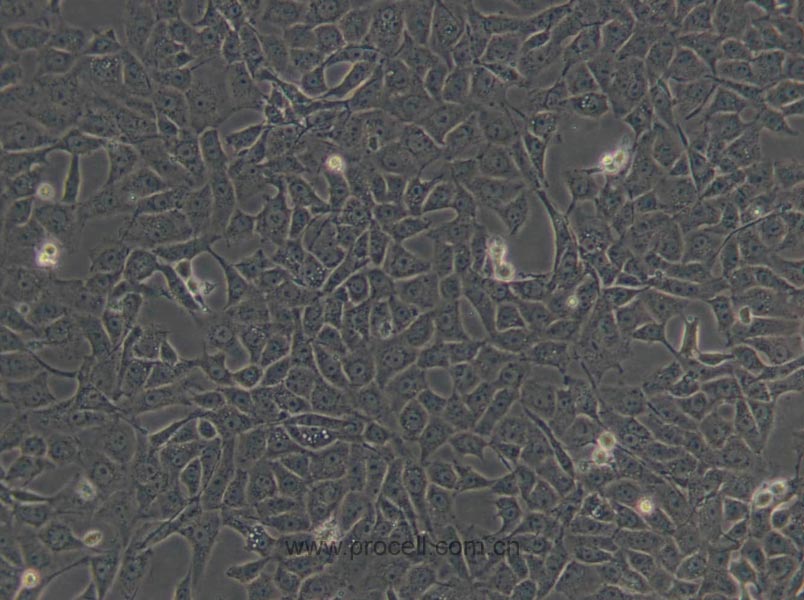
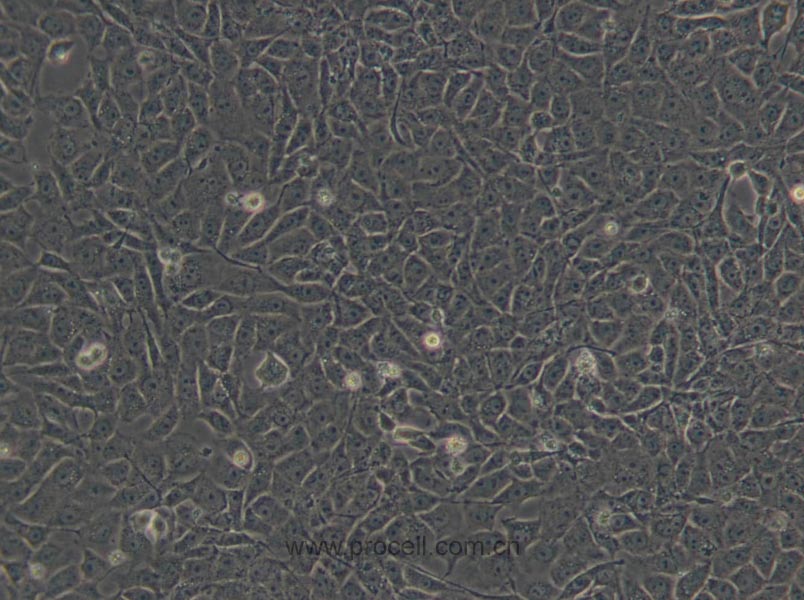
| 细胞形态 | 上皮细胞样 |
| 冻存条件 | 冻存液:55% 基础培养基+40%FBS+5%DMSO 温度:液氮 |
| 培养方案A(默认) |
培养条件:
气相:空气,95%;CO2,5%, 温度:37℃
|
| 推荐传代比例 | 1:2-1:4 |
| 推荐换液频率 | 2-3次/周 |
| 组织来源 | 肝 |
| 细胞类型 | 自发永生化细胞 |
| 生物安全等级 | BSL-1 |
| 保藏机构 | RCB; RCB0273 |
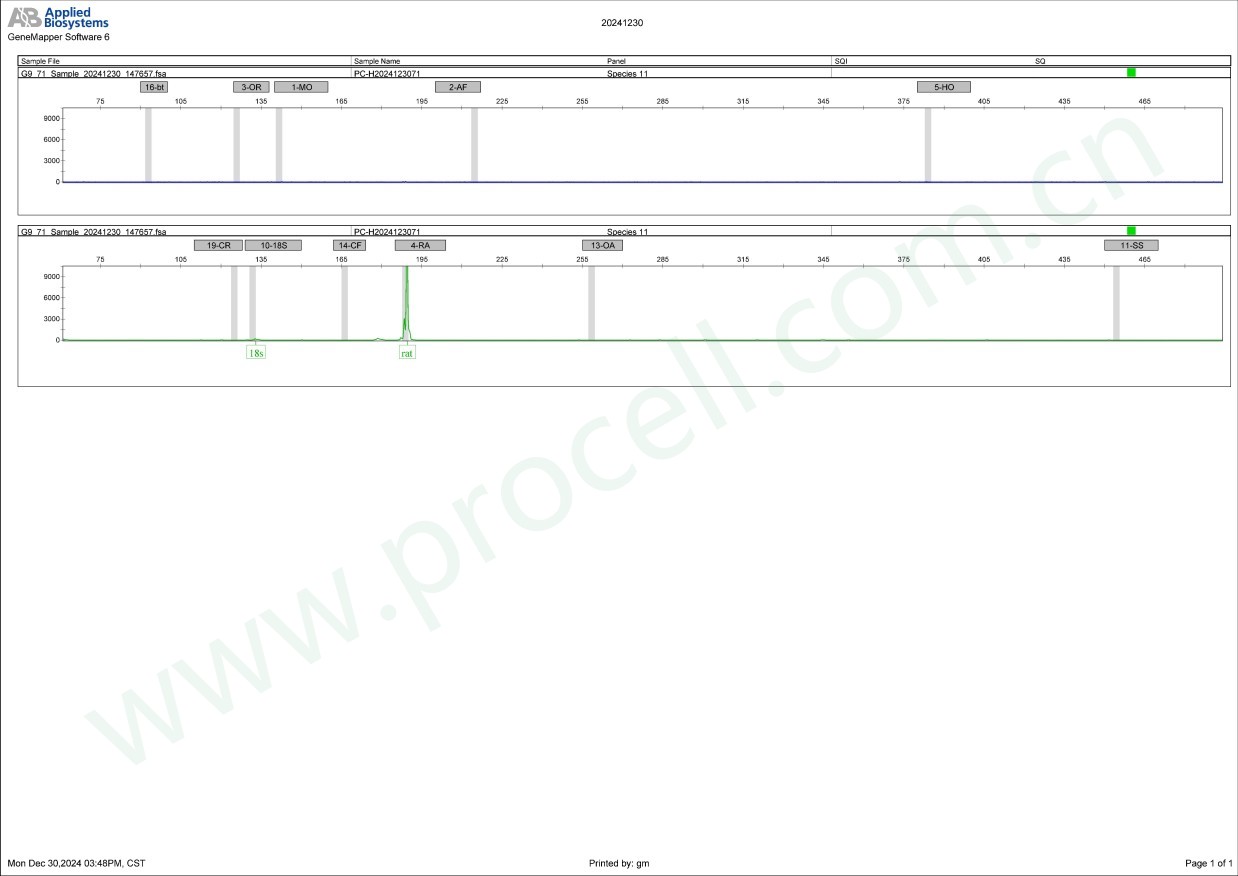
种属鉴定
-
种属鉴定图
-
参考文献
-
S-amlodipine induces liver inflammation and dysfunction through the alteration of intestinal microbiome in a rat model (2024-02-24)
期刊:Gut Microbes
DOI:10.1080/19490976.2024.2316923
影响因子 :12.2
-
Vitamin D3 improved hypoxia-induced lung injury by inhibiting the complement and coagulation cascade and autophagy pathway (2024-01-02)
期刊:BMC Pulmonary Medicine
DOI:10.1186/s12890-023-02784-y
影响因子 :3.1
引用产品: 大鼠Ⅱ型肺泡上皮细胞 , BRL 细胞
-
Maternal protein deficiency impairs peroxisome biogenesis and leads to oxidative stress and ferroptosis in liver of fetal growth restriction offspring (2023-08-30)
期刊:JOURNAL OF NUTRITIONAL BIOCHEMISTRY
DOI:10.1016/j.jnutbio.2023.109432
影响因子 :5.6
引用产品: BRL 细胞
-
Core–Shell Filament with Excellent Wound Healing Property Made of Cellulose Nanofibrils and Guar Gum via Interfacial Polyelectrolyte Complexation Spinning (2022-11-26)
期刊:Small
影响因子 :15.2
引用产品: EA.hy926 细胞 , BRL 细胞
-
Nrf2 and its dependent autophagy activation cooperatively counteract ferroptosis to alleviate acute liver injury (2022-11-21)
期刊:PHARMACOLOGICAL RESEARCH
DOI:10.1016/j.phrs.2022.106563
影响因子 :10.3
引用产品: BRL 细胞
-
Network pharmacology-based prediction of active compounds in the Wenyang Jiedu Huayu formula acting on acute-on-chronic liver failure with experimental support in vitro and in vivo (2022-10-20)
期刊:Frontiers in Pharmacology
DOI:10.3389/fphar.2022.1003479
影响因子 :6.0
引用产品: BRL 细胞
FAQs
Q:{{item.question}}
A:
产品资料


识别码示意图




![NR8383 [AgC11x3A; NR8383.1] (大鼠肺泡巨噬细胞) (种属鉴定正确)](/Public/upfile/pic/xbx/CL-0172-1.jpg)