产品中心Cell Resources
联系我们CONTACT US
 400-999-210024小时服务热线
400-999-210024小时服务热线
产品概述
| 名称 | EA.hy926 (人脐静脉细胞融合细胞) (STR鉴定正确) |
| 别称 | EA. hy 926; EA hy 926; EAhy 926; EAHY-926; EA.Hy926; EA.hy926; EAhy926; EaHy926; Eahy926 |
| 种属 | 人 |
| 生长特性 | 贴壁细胞 |
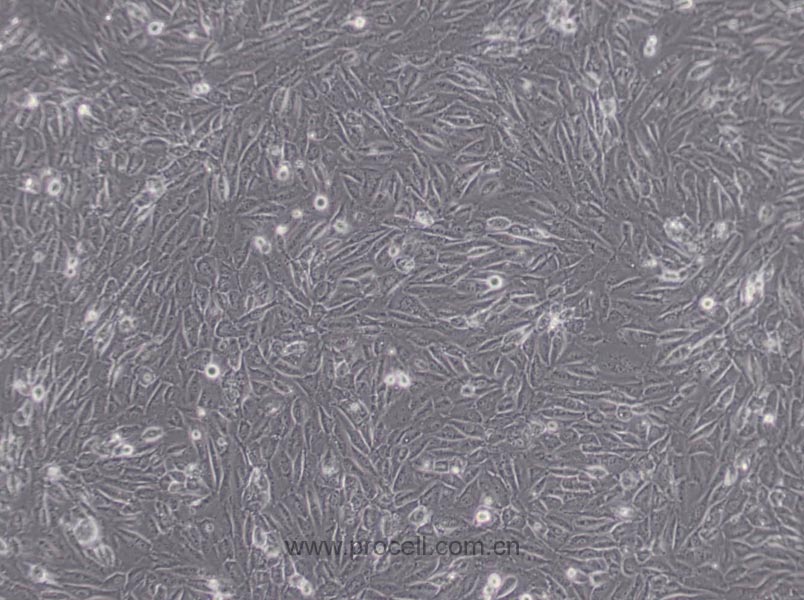
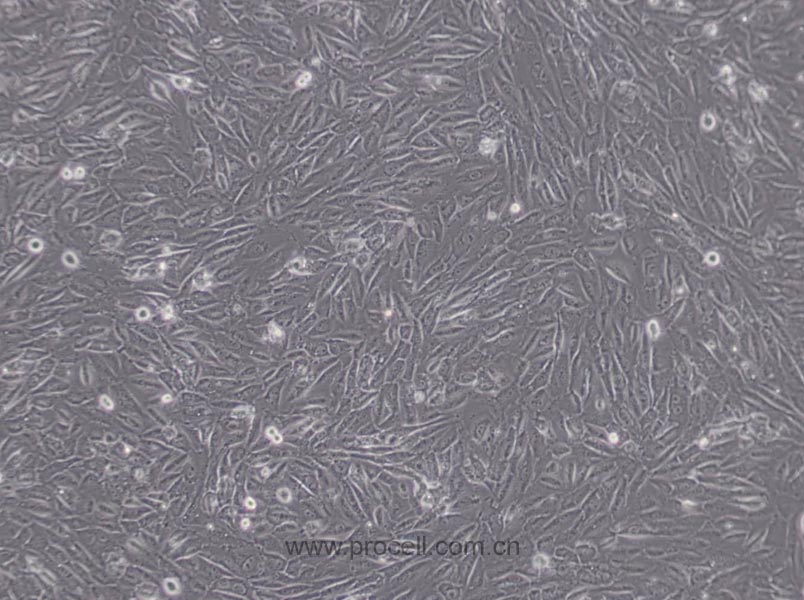
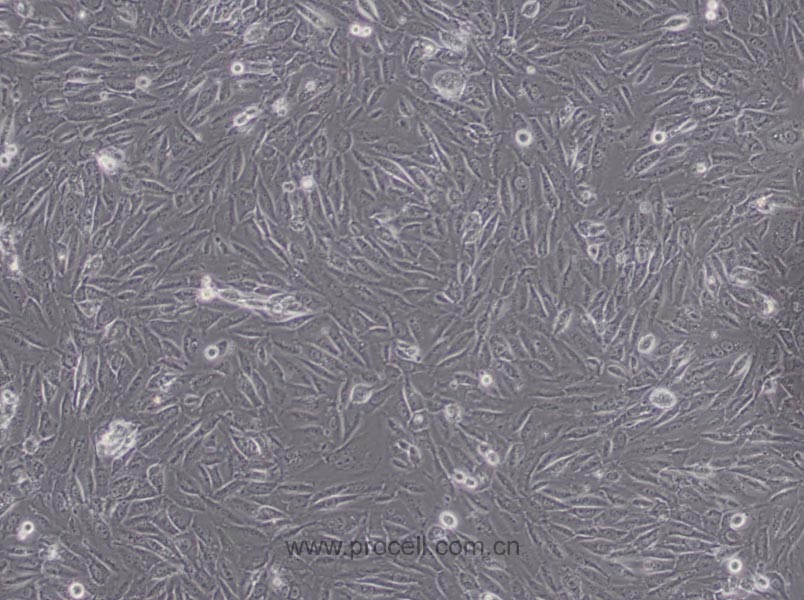
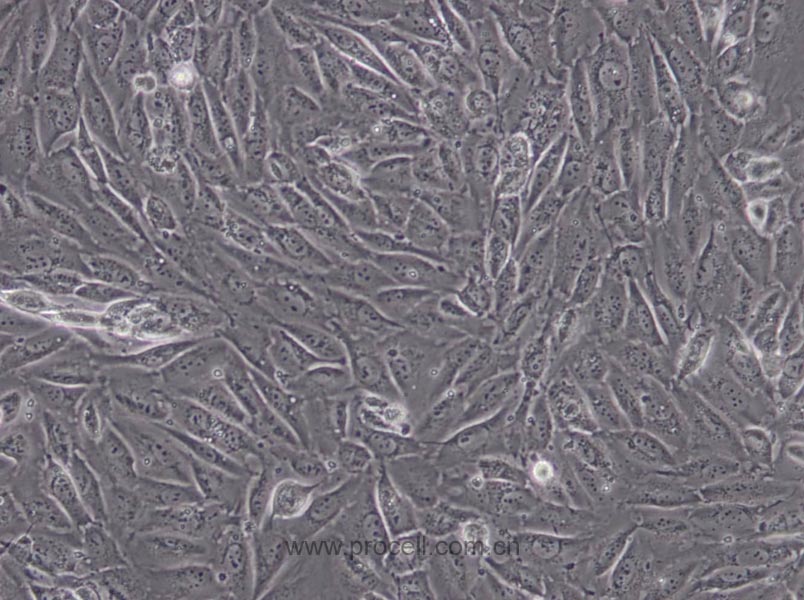
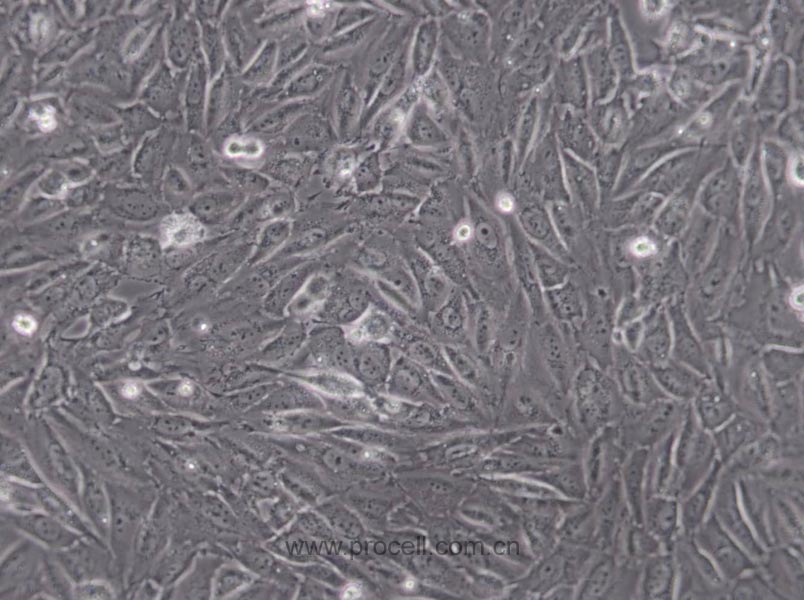
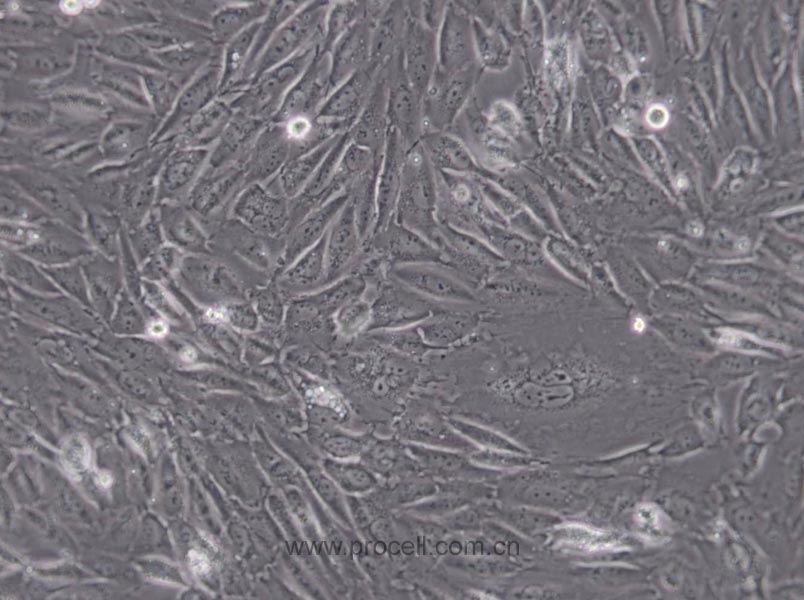
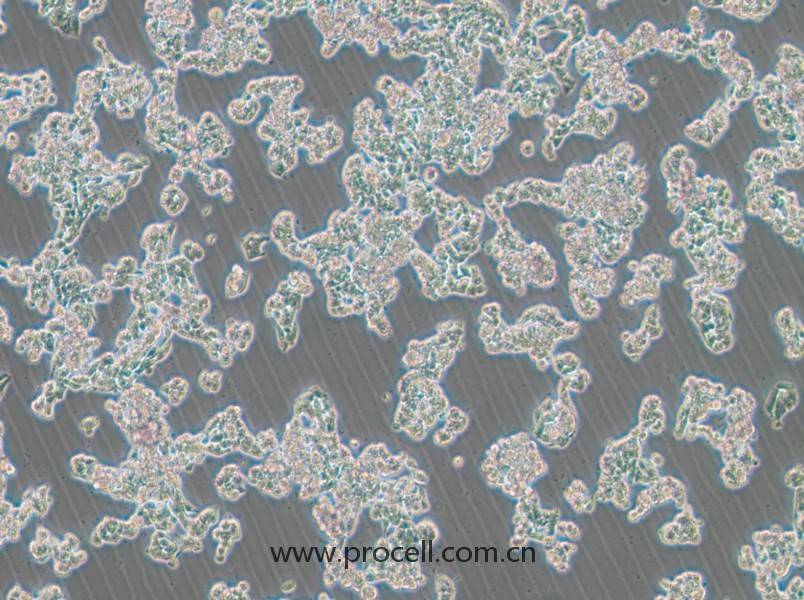
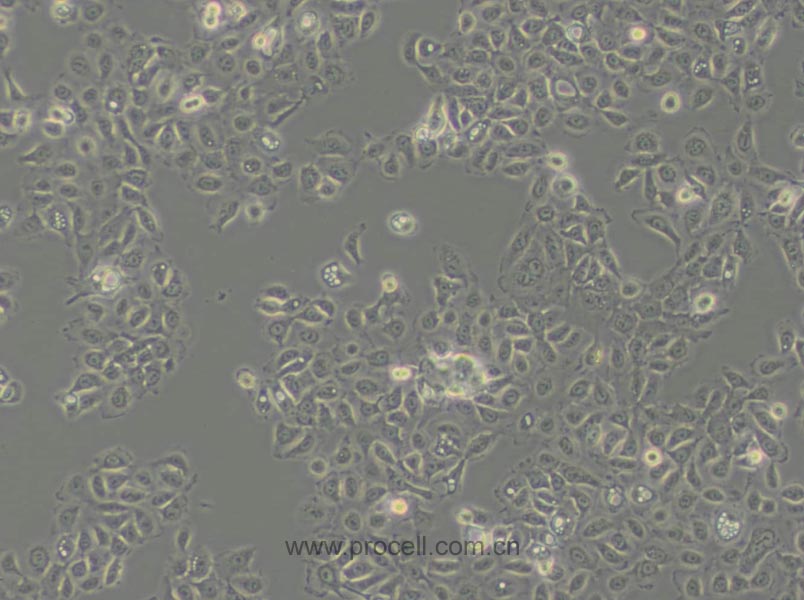
| 细胞形态 | 上皮细胞样 |
| 冻存条件 | 冻存液:55% 基础培养基+40%FBS+5%DMSO 温度:液氮 |
| 培养方案A(默认) |
培养条件:
气相:空气,95%;CO2,5%, 温度:37℃
|
| 推荐传代比例 | 1:3-1:4 |
| 推荐换液频率 | 2-3次/周 |
| 背景描述 | EA.hy926细胞是在PEG胁迫下,将原代培养的人脐静脉细胞与抗硫鸟嘌呤的A549克隆株融合,构建的一株人脐静脉细胞株。融合子在HAT培养基上生长,并以Ⅷ因子相关抗原筛选,EA.hy926细胞已经过100次以上的群体倍增(PDLs)。电镜照片显示,Weibel-Palade小体的细胞质分布以及组织特异性的细胞器,分化的内皮细胞特性如血管生成,体内平衡-血栓形成,血压及炎症反应。 |
| 组织来源 | 脐静脉/体细胞杂交 |
| 细胞类型 | 杂交瘤细胞 |
| 生物安全等级 | BSL-1 |
| 倍增时间 | ~12-24 hours |
| 抗原表达情况 | Factor VIII-related antigen; Homo sapiens, expressed |
| 基因表达情况 | Factor VIII-related antigen; Homo sapiens. |
| 保藏机构 | ATCC; CRL-2922 |
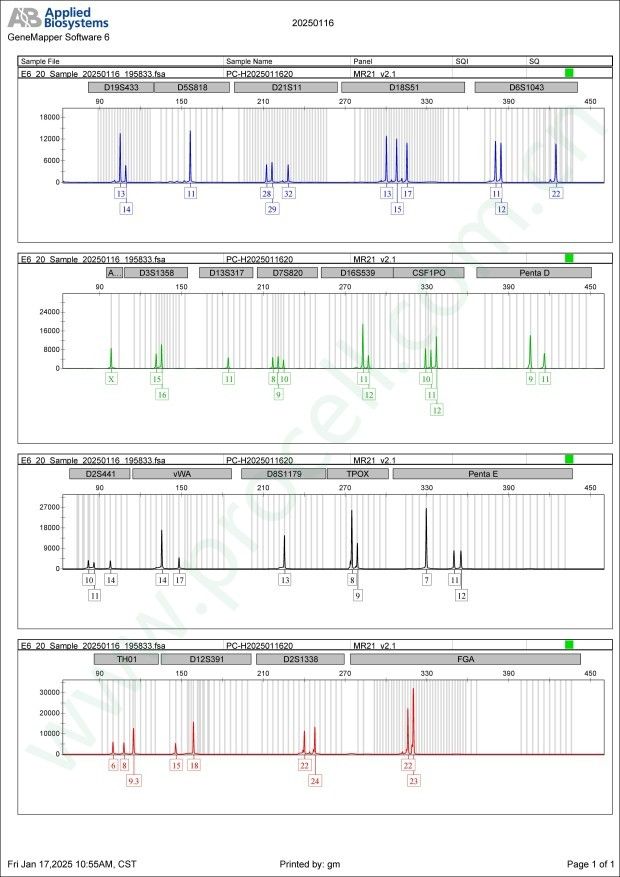
STR鉴定
-
STR位点信息
Amelogenin X CSF1PO 10,11,12 D2S1338 22,24 D3S1358 15,16 D5S818 11 D7S820 8,9,10 D8S1179 13 D13S317 11 D16S539 11,12 D18S51 13,15,17 D19S433 13,14 D21S11 28,29,32 FGA 22,23 PentaD 9,11 PentaE 7,11,12 TH01 6,8,9.3 TPOX 8,9 vWA 14,17 D6S1043 11,12,22 D12S391 15,18 D2S441 10,11,14 -
STR鉴定图
-
参考文献
-
Magnesium-gallate MOF integrated conductive cryogel for inflammation regulation and boosting bone regeneration (2025-03-03)
期刊:INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF BIOLOGICAL MACROMOLECULES
DOI:10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2025.141672
影响因子 :7.7
引用产品: 青霉素-链霉素溶液(双抗),100× , EA.hy926 细胞
-
GelMA@LNP/AST Promotes eNOS-Dependent Angiogenesis Through Autophagy Activation for the Treatment of Hind Limb Ischemia (2025-02-11)
期刊:International Journal of Nanomedicine
影响因子 :6.6
引用产品: EA.hy926 细胞
-
Trp31 Residue of Trx-1 Is Essential for Maintaining Antioxidant Activity and Cellular Redox Defense Against Oxidative Stress (2025-02-24)
期刊:Antioxidants
影响因子 :6.0
引用产品: EA.hy926 细胞 , EA.hy926细胞完全培养基
-
Angiogenic factor AGGF1 is a general splicing factor regulating angiogenesis and vascular development by alternative splicing of SRSF6 (2025-03-04)
期刊:FASEB JOURNAL
影响因子 :4.4
引用产品: 人肺大动脉内皮细胞 , EA.hy926 细胞 , 青霉素-链霉素溶液(双抗),100× , Hela 细胞 , 特级胎牛血清
-
Balancing Bioresponsive Biofilm Eradication and Guided Tissue Repair via Pro-Efferocytosis and Bidirectional Pyroptosis Regulation during Implant Surgery (2024-05-08)
期刊:ACS Nano
影响因子 :15.8
引用产品: EA.hy926 细胞 , NCTC clone 929 [L cell, L-929] 细胞 , Jurkat, Clone E6-1 细胞
-
Identification and characterization of umami-ACE inhibitory peptides from traditional fermented soybean curds (2024-11-20)
期刊:FOOD CHEMISTRY
DOI:10.1016/j.foodchem.2024.142160
影响因子 :8.5
引用产品: 青霉素-链霉素溶液(双抗),100× , 特级胎牛血清 , DMEM高糖 培养基 , EA.hy926 细胞
-
Chondroitin sulfate-modified antiangiogenic peptide conjugate induces cell apoptosis via the mitochondria-mediated pathway to perform antitumor activity (2024-02-29)
期刊:INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF BIOLOGICAL MACROMOLECULES
DOI:10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2024.129671
影响因子 :8.2
引用产品: EA.hy926 细胞
-
Dynamic RGD ligands derived from highly mobile cyclodextrins regulate spreading and proliferation of endothelial cells to promote vasculogenesis (2024-04-16)
期刊:INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF BIOLOGICAL MACROMOLECULES
DOI:10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2024.131667
影响因子 :8.2
引用产品: EA.hy926 细胞 , 人真皮成纤维细胞 , DMEM高糖 培养基
-
Enhancing cellular behavior in repaired tissue via silk fibroin-integrated triboelectric nanogenerators (2024-05-24)
期刊:Microsystems & Nanoengineering
DOI:10.1038/s41378-024-00694-5
影响因子 :7.9
引用产品: EA.hy926 细胞 , RSC96 细胞 , NIH/3T3 细胞
-
3D-printed biomimetic bone scaffold loaded with lyophilized concentrated growth factors promotes bone defect repair by regulation the VEGFR2/PI3K/AKT signaling pathway (2024-10-26)
期刊:INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF BIOLOGICAL MACROMOLECULES
DOI:10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2024.136938
影响因子 :7.7
引用产品: EA.hy926 细胞
-
Osteo-angiogenic activity of a micro/nano hierarchical SrSi-codoped hydroxyapatite coating on zirconium alloy (2024-05-13)
期刊:Journal of Materials Research and Technology-JMR&T
DOI:10.1016/j.jmrt.2024.05.067
影响因子 :6.4
-
Identification and in silico screening of Novel Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme Inhibitory Peptides from Pacific saury: Interaction mechanism, Network pharmacology, Stability, Caco-2 monolayer transport (2024-06-18)
期刊:Food Bioscience
DOI:10.1016/j.fbio.2024.104576
影响因子 :4.8
引用产品: Caco-2 细胞 , EA.hy926 细胞
-
Porphyromonas gingivalis OMVs promoting endothelial dysfunction via the STING pathway in periodontitis (2024-05-02)
期刊:ORAL DISEASES
影响因子 :3.8
引用产品: MEMα 培养基 , MG-63 细胞 , 特级胎牛血清 , EA.hy926 细胞 , DMEM高糖 培养基
-
Effect of High Magnesium and Astragaloside IV on Vascular Endothelial Cells (2024-05-09)
期刊:CELL BIOCHEMISTRY AND BIOPHYSICS
DOI:10.1007/s12013-024-01250-8
影响因子 :2.6
引用产品: EA.hy926 细胞
-
Human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells overexpressing RUNX1 promote tendon-bone healing by inhibiting osteolysis, enhancing osteogenesis and promoting angiogenesis (2024-01-05)
期刊:Genes & Genomics
DOI:10.1007/s13258-023-01478-3
影响因子 :2.1
引用产品: THP-1 细胞 , 人脐带间充质干细胞 , EA.hy926 细胞 , 青霉素-链霉素溶液 (双抗),100× , 人脐带间充质干细胞成骨诱导分化培养基
-
Endothelial discoidin domain receptor 1 senses flow to modulate YAP activation (2023-10-13)
期刊:Nature Communications
DOI:10.1038/s41467-023-42341-z
影响因子 :16.6
引用产品: EA.hy926 细胞 , NIH/3T3 细胞
-
Inflammation-Responsive Hydrogel Spray for Synergistic Prevention of Traumatic Heterotopic Ossification via Dual-Homeostatic Modulation Strategy (2023-08-27)
期刊:Advanced Science
影响因子 :15.1
引用产品: RAW 264.7 细胞 , 小鼠肌腱干细胞 , C2C12 细胞 , NCTC clone 929 [L cell, L-929] 细胞 , EA.hy926 细胞 , MC3T3-E1 Subclone 24 细胞
-
CD44 targeting nanodrug based on chondroitin sulfate for melanoma therapy by inducing mitochondrial apoptosis pathways (2023-08-02)
期刊:CARBOHYDRATE POLYMERS
DOI:10.1016/j.carbpol.2023.121255
影响因子 :11.2
引用产品: EA.hy926 细胞 , B16 细胞
-
Bioinspired, Robust, and Absorbable Cellulose Nanofibrils/Chitosan Filament with Remarkable Cytocompatibility and Wound Healing Properties (2023-09-06)
期刊:ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces
影响因子 :9.5
引用产品: EA.hy926 细胞
-
Fabrication and performance evaluation of PLCL-hCOLIII small-diameter vascular grafts crosslinked with procyanidins (2023-08-15)
期刊:INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF BIOLOGICAL MACROMOLECULES
DOI:10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2023.126293
影响因子 :8.2
引用产品: EA.hy926 细胞
-
Biomimetic nanoplatform with selectively positioned indocyanine green for accurate sentinel lymph node imaging (2023-11-16)
期刊:Nanoscale
影响因子 :6.7
引用产品: RAW 264.7 细胞 , EA.hy926 细胞
-
PLA-HPG based coating enhanced anti-biofilm and wound healing of Shikonin in MRSA-infected burn wound (2023-08-10)
期刊:Frontiers in Bioengineering and Biotechnology
DOI:10.3389/fbioe.2023.1243525
影响因子 :5.7
-
Study on the effect of type III recombinant humanized collagen on human vascular endothelial cells (2023-11-29)
期刊:Tissue Engineering Part C-Methods
影响因子 :3.0
引用产品: EA.hy926 细胞
-
Modification of the small intestinal submucosa membrane with oligopeptides screened from intrinsically disordered regions to promote angiogenesis and accelerate wound healing (2023-03-02)
期刊:Biomaterials Advances
DOI:10.1016/j.bioadv.2023.213360
影响因子 :0.0
引用产品: EA.hy926 细胞
-
Core–Shell Filament with Excellent Wound Healing Property Made of Cellulose Nanofibrils and Guar Gum via Interfacial Polyelectrolyte Complexation Spinning (2022-11-26)
期刊:Small
影响因子 :15.2
引用产品: EA.hy926 细胞 , BRL 细胞
-
A dual Keap1 and p47phox inhibitor Ginsenoside Rb1 ameliorates high glucose/ox-LDL-induced endothelial cell injury and atherosclerosis (2022-09-26)
期刊:Cell Death & Disease
DOI:10.1038/s41419-022-05274-x
影响因子 :9.7
引用产品: EA.hy926 细胞
-
Carboxy-terminal telopeptide levels of type I collagen hydrogels modulated the encapsulated cell fate for regenerative medicine (2022-12-22)
期刊:INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF BIOLOGICAL MACROMOLECULES
DOI:10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2022.12.186
影响因子 :8.0
引用产品: EA.hy926 细胞
-
Osteo-angiogenic and antibacterial activity of a multifunctional micro-porous coating on zirconium alloy (2022-08-06)
期刊:APPLIED SURFACE SCIENCE
DOI:10.1016/j.apsusc.2022.154465
影响因子 :7.4
引用产品: MC3T3-E1 Subclone 24 细胞 , EA.hy926 细胞
-
Salvianolic Acid Ameliorates Pressure Overload-Induced Cardiac Endothelial Dysfunction via Activating HIF1α/HSF1/CD31 Pathway (2022-09-17)
期刊:AMERICAN JOURNAL OF CHINESE MEDICINE
影响因子 :6.0
引用产品: EA.hy926 细胞
-
Platelet-rich plasma promotes diabetic ulcer repair through inhibition of ferroptosis (2022-10-01)
期刊:Annals of Translational Medicine
影响因子 :3.6
引用产品: 人真皮成纤维细胞 , EA.hy926 细胞
-
Chimeric Peptides Quickly Modify the Surface of Personalized 3D Printing Titanium Implants to Promote Osseointegration (2021-07-14)
期刊:ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces
影响因子 :9.5
引用产品: EA.hy926 细胞
FAQs
Q:{{item.question}}
A:
产品资料


识别码示意图