产品中心Cell Resources
联系我们CONTACT US
 400-999-210024小时服务热线
400-999-210024小时服务热线
产品概述
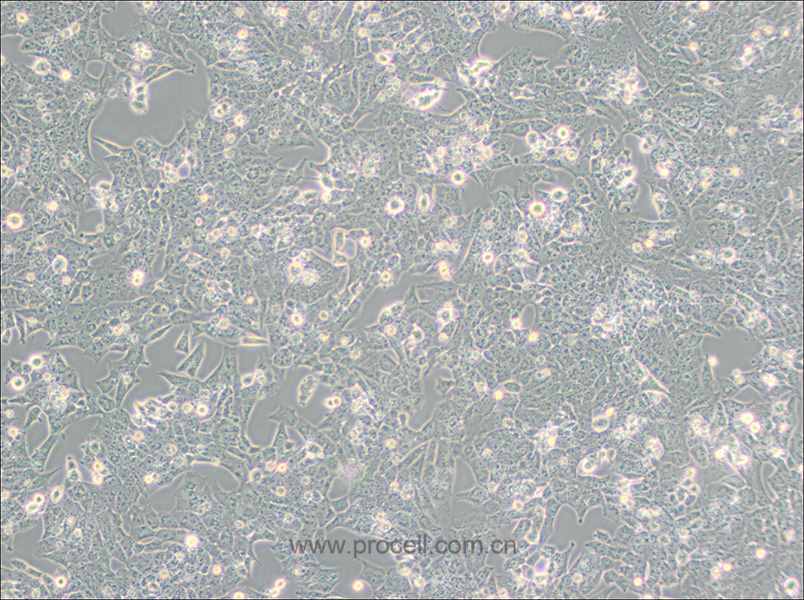
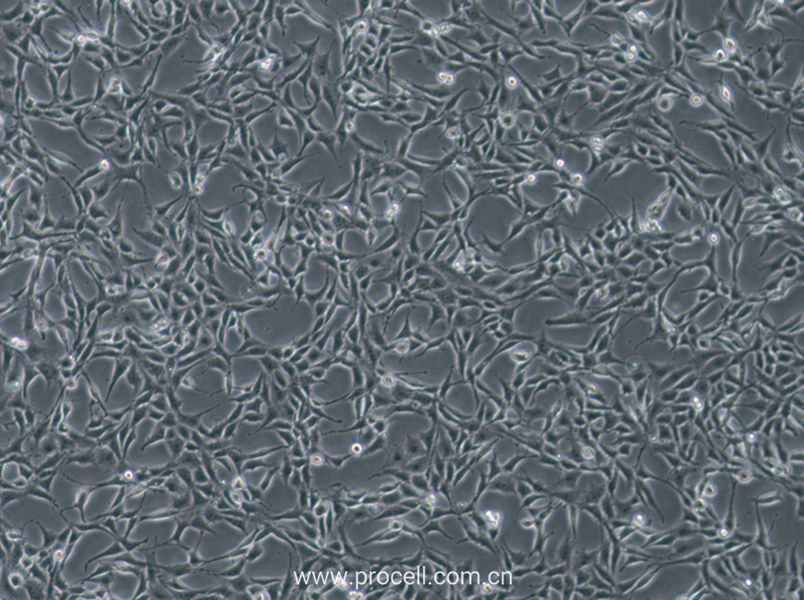
| 名称 | RBL-2H3 (大鼠嗜碱性细胞白血病细胞) (种属鉴定正确) |
| 别称 | RBL2H3; RBL 2H3; RBL.2H3 |
| 种属 | 大鼠 |
| 生长特性 | 贴壁细胞 |
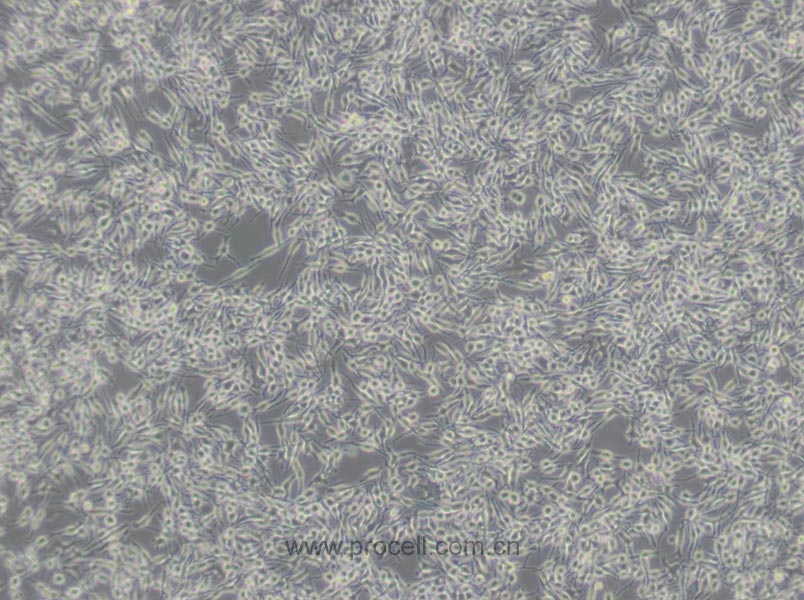
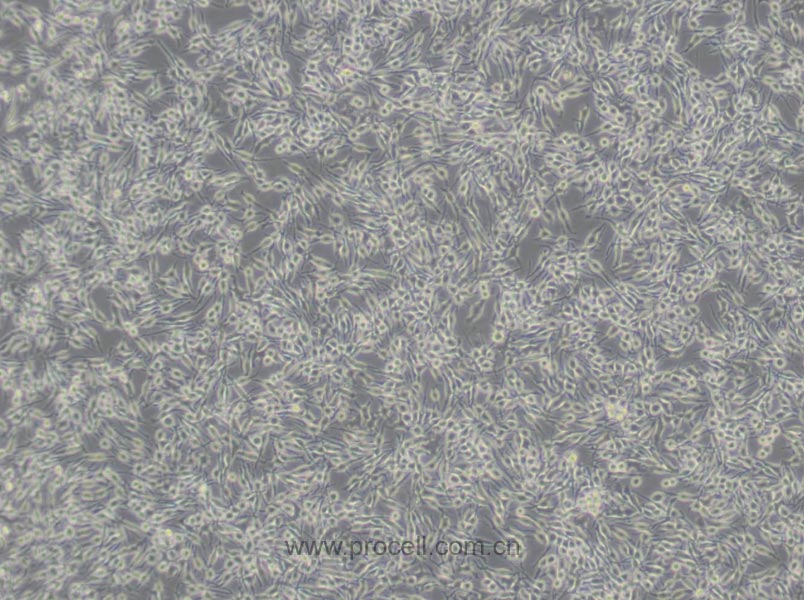
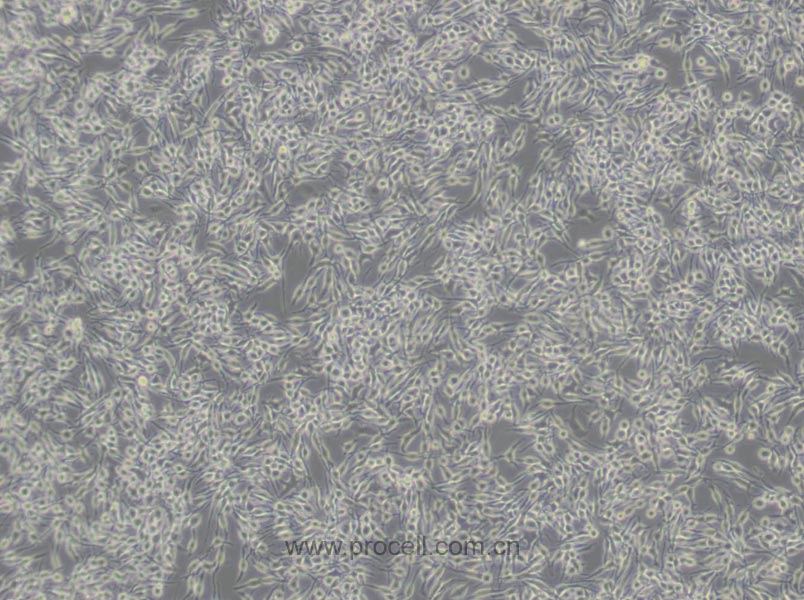
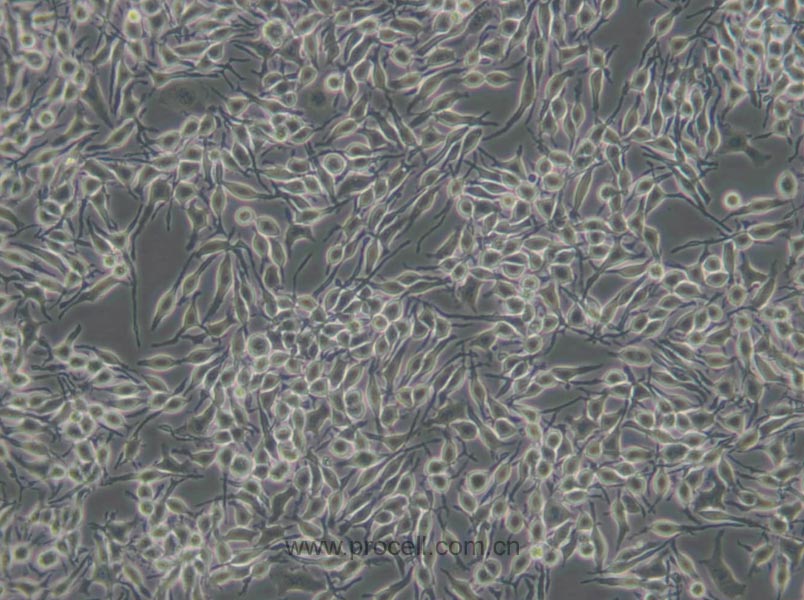
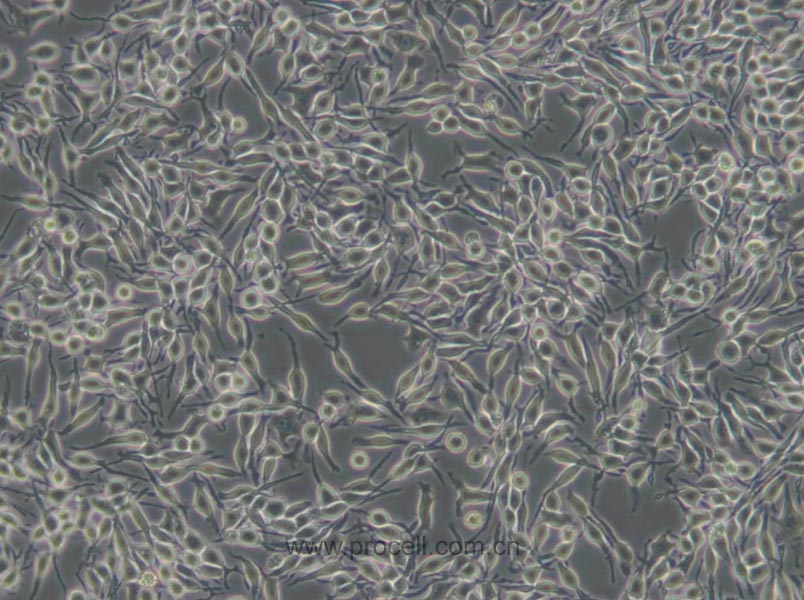
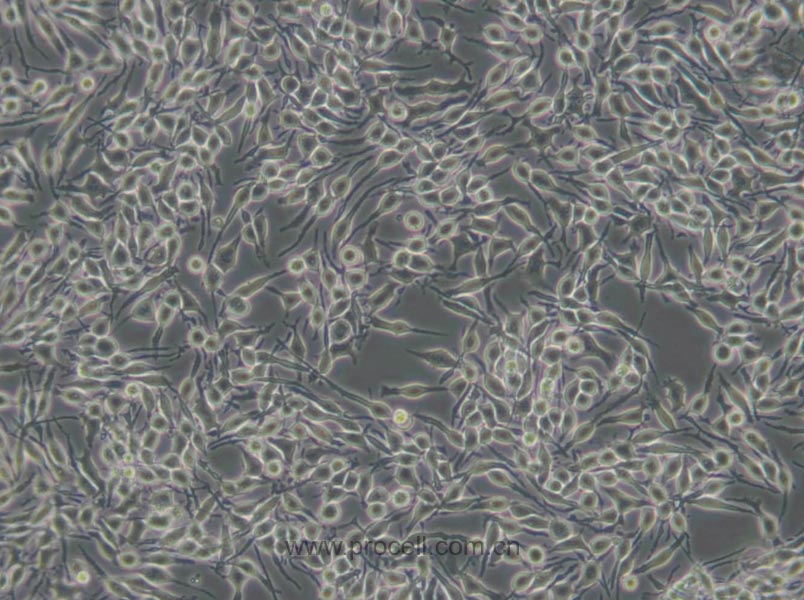
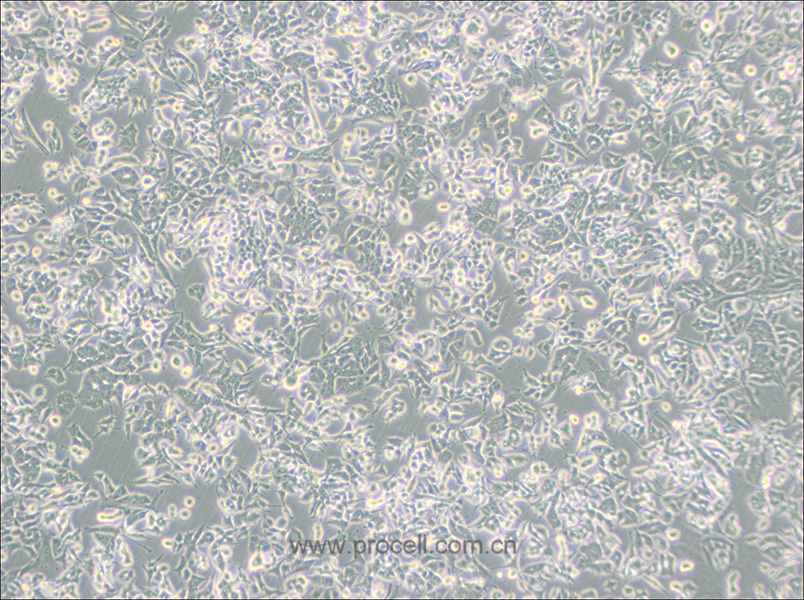
| 细胞形态 | 成纤维细胞样 |
| 冻存条件 | 冻存液:55% 基础培养基+40%FBS+5%DMSO 温度:液氮 |
| 培养方案A(默认) |
生长培养基:
培养条件:
气相:空气,95%;CO2,5%, 温度:37℃
|
| 推荐传代比例 | 1:3-1:6 |
| 推荐换液频率 | 2-3次/周 |
| 背景描述 | RBL-2H3细胞是1978年国立牙科研究所的免疫学实验室从Wistar大鼠保持肿瘤状态的嗜碱性细胞中分离和克隆出来的嗜碱性白血病细胞株。RBL-2H3细胞具有高亲和力的IgE受体,通过集聚这些受体或与钙离子载体协同作用可以激活它们分泌组胺及其他递质。RBL-2H3细胞广泛地用于研究肥大细胞FcERI和分泌的生化途径。RBL-2H3细胞是研究FcERI结构的模型。它们广泛地用于研究细胞分泌的不同方面,包括细胞内钙浓度改变、磷酸脂酶激活、蛋白激酶和小G蛋白的作用。虽然几乎所有批号的FBS都支持细胞的生长,但在某些批号中FcERI集聚后脱粒化得更好。另一株大鼠嗜碱性细胞株(RBL)不会脱粒化。 |
| 组织来源 | 外周血;化学诱变嗜碱性细胞;白血病 |
| 细胞类型 | 肿瘤细胞 |
| 肿瘤类型 | 白血病细胞 |
| 生物安全等级 | BSL-1 |
| 倍增时间 | ~50-60 hours |
| 受体表达情况 | FcERI (Fc of IgE) |
| 基因表达情况 | histamine |
| 保藏机构 | ATCC; CRL-2256 DSMZ; ACC-312 |
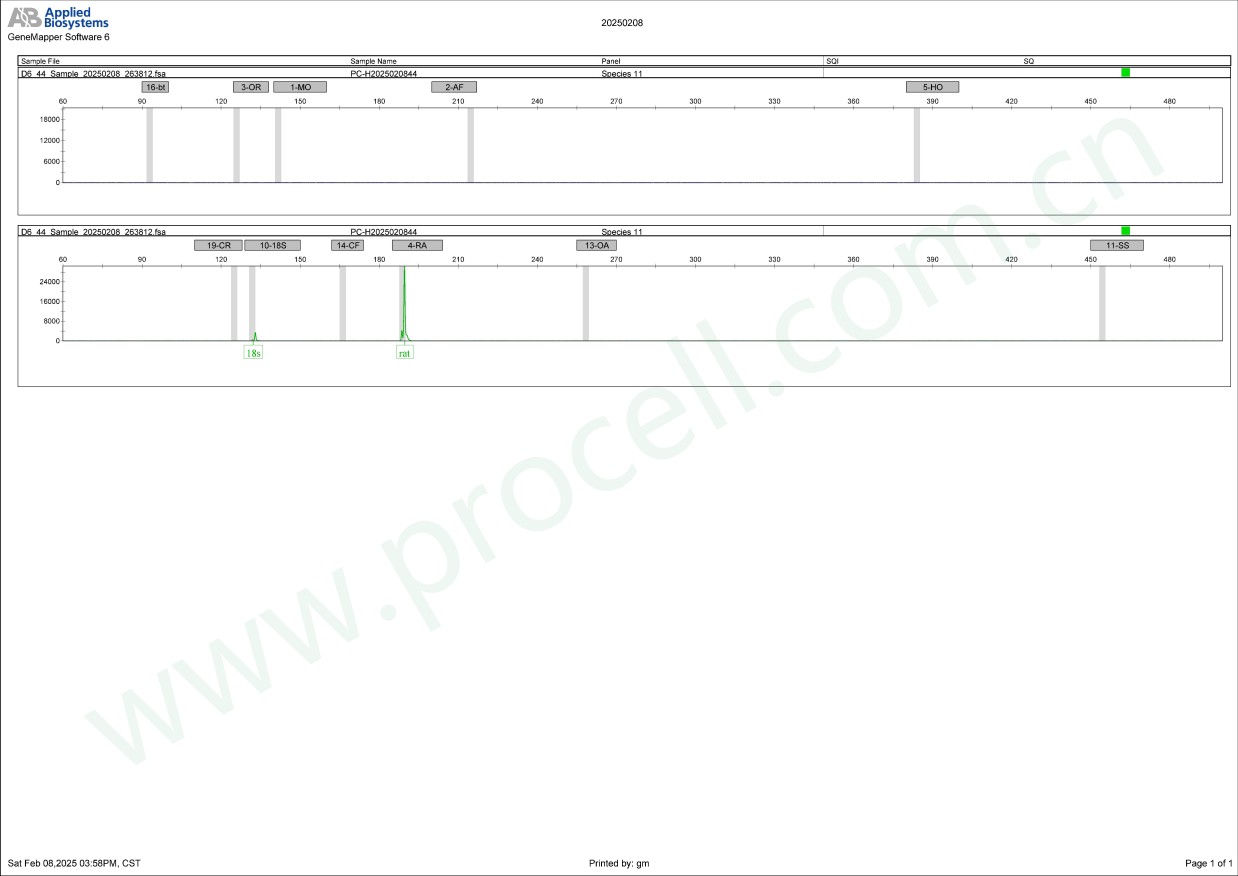
种属鉴定
-
种属鉴定图
-
参考文献
-
Current utilization trend of immortalized mast cell lines in allergy research: a systematic review (2025-01-21)
期刊:IMMUNOLOGIC RESEARCH
DOI:10.1007/s12026-024-09562-w
影响因子 :3.3
引用产品: RBL-2H3 细胞
-
SERT and OCT mediate 5-HT1B receptor regulation of immobility behavior and uptake of 5-HT and HIS (2024-06-24)
期刊:BIOMEDICINE & PHARMACOTHERAPY
DOI:10.1016/j.biopha.2024.117017
影响因子 :6.9
引用产品: RBL-2H3 细胞
-
Modulation of soy protein immunoreactivity by different matrix structures of lactic acid bacterium-induced soy protein gels: Epitope destruction during in vitro gastroduodenal digestion and absorption (2023-07-16)
期刊:FOOD RESEARCH INTERNATIONAL
DOI:10.1016/j.foodres.2023.113281
影响因子 :8.1
引用产品: RBL-2H3 细胞
-
Insight into the conformational and allergenicity alterations of shrimp tropomyosin induced by Sargassum fusiforme polyphenol (2023-01-25)
期刊:FOOD RESEARCH INTERNATIONAL
DOI:10.1016/j.foodres.2023.112521
影响因子 :8.1
引用产品: RBL-2H3 细胞
-
Assessment of the effect of glycation on the allergenicity of sesame proteins (2023-03-26)
期刊:FOOD RESEARCH INTERNATIONAL
DOI:10.1016/j.foodres.2023.112771
影响因子 :8.1
引用产品: 特级胎牛血清 , 青霉素-链霉素-两性霉素B溶液 (100×) , RBL-2H3 细胞
-
Investigation of the allergenicity alterations of shrimp tropomyosin as glycated by glucose and maltotriose containing advanced glycation end products (2023-11-15)
期刊:Food & Function
影响因子 :6.1
引用产品: RBL-2H3 细胞
-
Molecular docking, network pharmacology and experimental verification to explore the mechanism of Wulongzhiyangwan in the treatment of pruritus (2023-01-07)
期刊:Scientific Reports
DOI:10.1038/s41598-023-27593-5
影响因子 :4.6
引用产品: RBL-2H3 细胞
-
Anti-Allergic Effect of Dietary Polyphenols Curcumin and Epigallocatechin Gallate via Anti-Degranulation in IgE/Antigen-Stimulated Mast Cell Model: A Lipidomics Perspective (2023-05-05)
期刊:Metabolites
影响因子 :4.1
引用产品: RBL-2H3 细胞
-
A fibrin Site-Specific Nanoprobe for Imaging Fibrin-Rich Thrombi and Preventing Thrombus Formation in Venous Vessels (2022-03-14)
期刊:Advanced Materials
影响因子 :32.1
引用产品: RBL-2H3 细胞
-
Study of the in vitro properties of oligopeptides from whey protein isolate with high Fisher's ratio and their ability to prevent allergic response to β-lactoglobulin in vivo (2022-11-03)
期刊:FOOD CHEMISTRY
DOI:10.1016/j.foodchem.2022.134841
影响因子 :9.2
引用产品: RAW 264.7 细胞 , RBL-2H3 细胞
-
Adenosine cyclic phosphate with ultrasonic-assisted pectinase extraction alleviated allergic reactions in RBL-2H3 through inhibiting the influx of intracellular Ca2+ (2022-10-15)
期刊:Food Science and Human Wellness
DOI:10.1016/j.fshw.2022.09.023
影响因子 :8.0
引用产品: RBL-2H3 细胞
-
A Metabolomics Study on the Bone Protective Effects of a Lignan-Rich Fraction From Sambucus Williamsii Ramulus in Aged Rats (2018-08-02)
期刊:Frontiers in Pharmacology
影响因子 :5.6
引用产品: RBL-2H3 细胞
FAQs
Q:{{item.question}}
A:
产品资料


识别码示意图