产品中心Cell Resources
联系我们CONTACT US
 400-999-210024小时服务热线
400-999-210024小时服务热线
产品概述
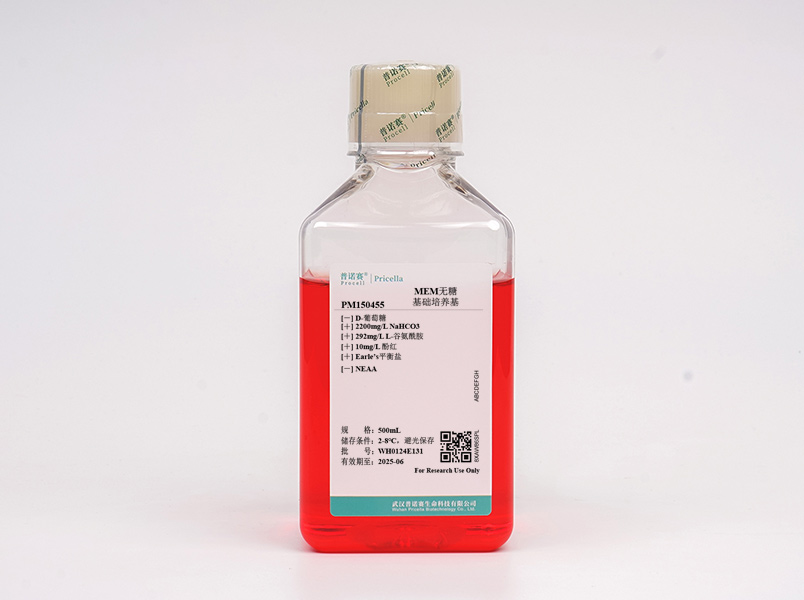
MEM培养基(Minimum Essential Medium)也称最低必需培养基、最小基本培养基或低限量Eagle培养基,由Harry Eagle在Eagle基本培养基(BEM)的基础上发展而来的,是一种最基本、适用范围最广的培养基,是动物细胞培养中最常用的培养基之一。MEM培养基仅含有12种必需氨基酸、谷氨酰胺和8种维生素,成分简单,主要用于贴壁细胞的培养,配方修改后也可用于其他类型细胞培养。
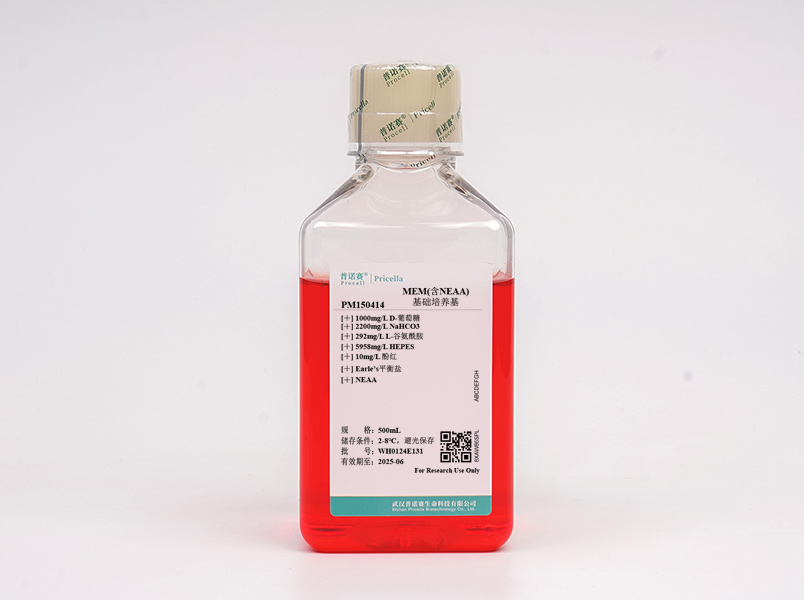
MEM含NEAA(非必须氨基酸)的培养基,是在MEM培养基的基础上添加L-丙氨酸、L-谷氨酸、L-天(门)冬酰胺、L-天(门)冬氨酸、L-脯氨酸、L-丝氨酸和甘氨酸7种NEAA,能降低细胞培养时细胞自身生产非必须氨基酸的副作用,有效促进细胞增殖代谢。不含葡萄糖的MEM培养基可以根据研究需要,随意调节葡萄糖的浓度,方便快捷。
本产品含有多类细胞培养所需的氨基酸、维生素、无机盐等多种成分,但不含蛋白质、脂类或任何生长因子,故此产品需搭配血清或无血清添加物使用。
成分说明
形态 | 液体 |
浓度 | 1× |
规格 | 500mL |
pH | 7.2-7.4 |
平衡盐 | Earle’s 盐 |
NEAA | 含 |
L-谷氨酰胺 | 2 mM |
NaHCO3 | 2200 mg/L |
D-葡萄糖 | 无 |
HEPES缓冲剂 | 无 |
酚红指示剂 | 10 mg/L |
储存条件 | 2-8℃,避光 |
运输条件 | 常温 |
有效期 | 18个月 |
注意事项
1、本产品经0.1 μm过滤除菌,使用时应注意无菌操作,避免污染;
2、为保持本产品的最佳使用效果,请勿进行冻融处理;
3、本产品仅用于科研或进一步研究使用,不用于诊断和治疗。
参考文献
-
Wnt5a in keratinocytes contributes to complex regional pain syndrome through the activation of NR2B and MMP9 in rats (2025-03-12)
期刊:REGIONAL ANESTHESIA AND PAIN MEDICINE
影响因子 :5.1
引用产品: MEM无糖(含NEAA) 培养基
-
NMDA Receptors Regulate Oxidative Damage in Keratinocytes during Complex Regional Pain Syndrome in HaCaT Cells and Male Rats (2024-02-18)
期刊:Antioxidants
影响因子 :7.0
引用产品: MEM无糖 (含NEAA) 培养基
-
TFE3-SLC36A1 axis promotes resistance to glucose starvation in kidney cancer cells (2024-04-08)
期刊:JOURNAL OF BIOLOGICAL CHEMISTRY
影响因子 :4.8
引用产品: ACHN 细胞 , DMEM无糖 培养基 , McCoy's 5A 培养基 , McCoy's 5A无糖 培养基 , MEM无糖(含NEAA) 培养基 , MEM(含NEAA) 培养基 , Caki-1 细胞
-
UBC9-mediated SUMOylation of Lamin B1 enhances DNA-damage-induced nuclear DNA leakage and autophagy after spinal cord injury (2024-02-03)
期刊:JOURNAL OF CELLULAR PHYSIOLOGY
影响因子 :4.5
引用产品: MEM(含NEAA) 培养基 , MEM无糖(含NEAA) 培养基
-
Human Umbilical Cord Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Derived Exosomes Attenuate Oxygen-Glucose Deprivation/Reperfusion-Induced Microglial Pyroptosis by Promoting FOXO3a-Dependent Mitophagy (2021-11-02)
期刊:Oxidative Medicine and Cellular Longevity
影响因子 :0.0
引用产品: MEM无糖 (含NEAA) 培养基
-
Autophagy alleviates hypoxia-induced blood-brain barrier injury via regulation of CLDN5 (claudin 5) (2020-12-07)
期刊:Autophagy
DOI:10.1080/15548627.2020.1851897
影响因子 :9.8
引用产品: MEM无糖(含NEAA) 培养基
FAQs
Q:{{item.question}}
A:
产品资料


识别码示意图