产品中心Cell Resources
联系我们CONTACT US
 400-999-210024小时服务热线
400-999-210024小时服务热线
产品概述
| 名称 | SK-MEL-1 (人皮肤黑色素瘤细胞) (STR鉴定正确) |
| 别称 | SK-Mel-1; SK Mel 1; SK-Mel 1; SK-Mel1; SKMEL-1; SkMEL-1; SKMEL1; SK 1 |
| 种属 | 人 |
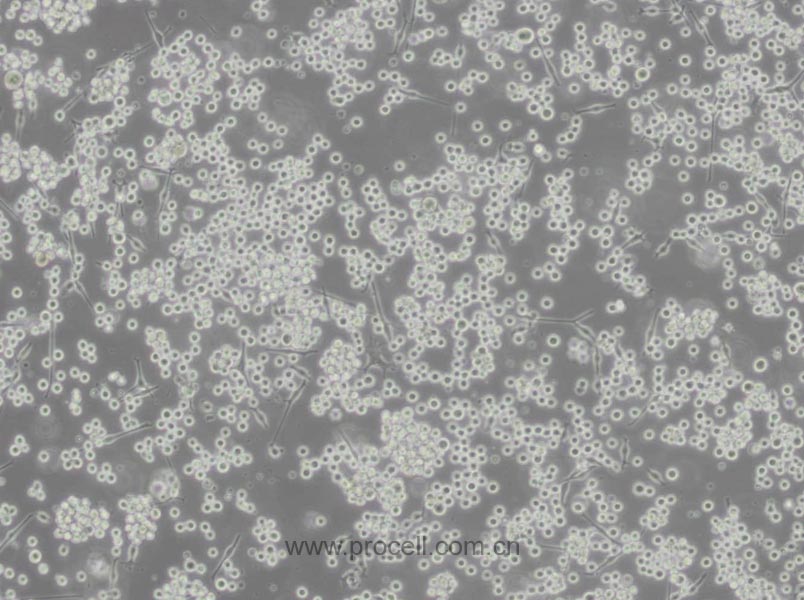
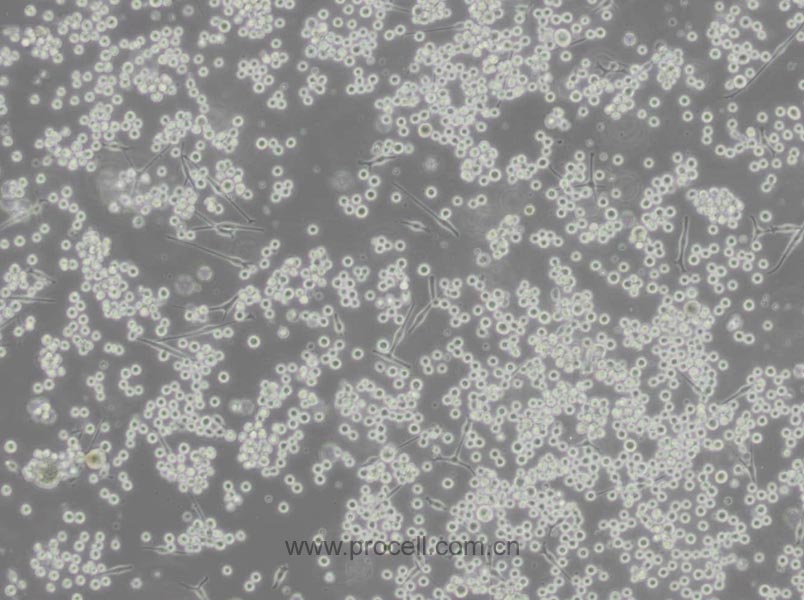
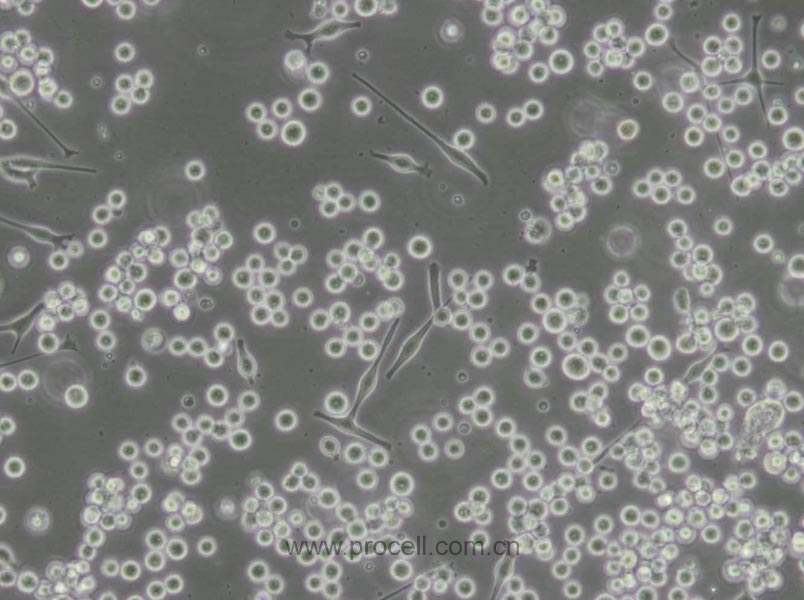
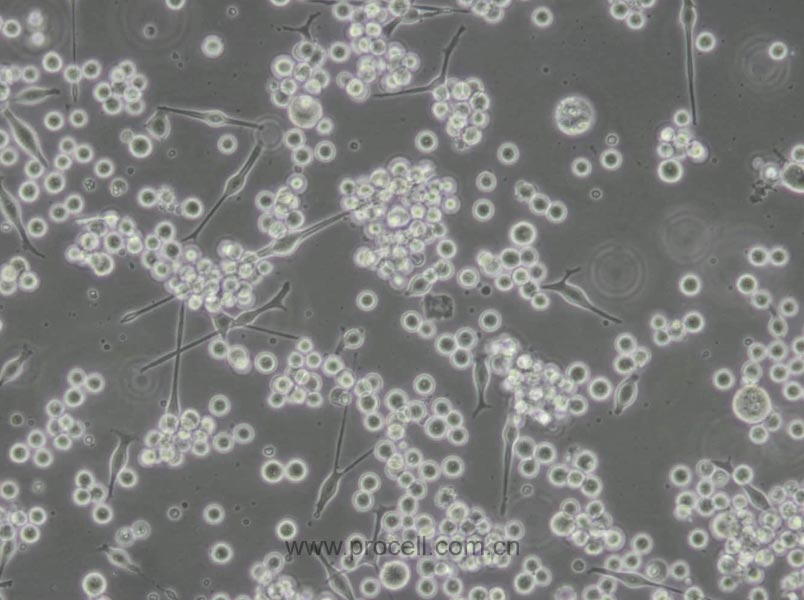
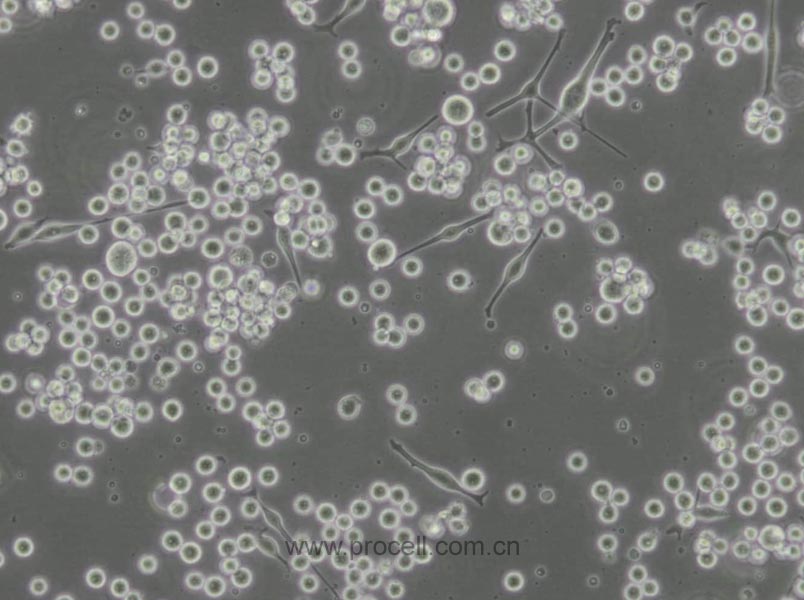
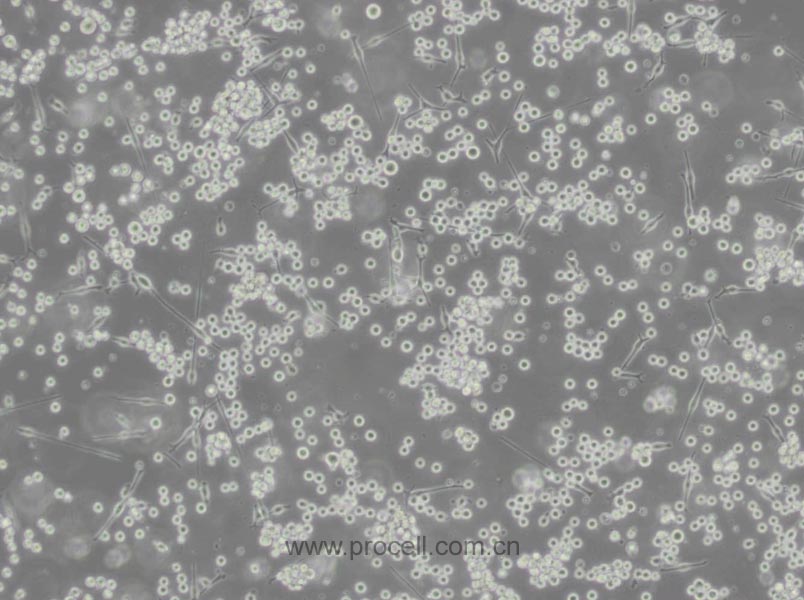
| 生长特性 | 悬浮细胞 |
| 细胞形态 | 球形 |
| 冻存条件 | 冻存液:55% 基础培养基+40%FBS+5%DMSO 温度:液氮 |
| 培养方案A(默认) |
生长培养基:
培养条件:
气相:空气,95%;CO2,5%, 温度:37℃
|
| 推荐传代比例 | 3×10^5-5×10^5cells/mL |
| 推荐换液频率 | 2-3次/周 |
| 注意事项 | 该细胞为悬浮细胞,请注意离心收集细胞悬液;请勿直接倒掉细胞培养液。 |
| 背景描述 | SK-MEL-1细胞由Oettgen·F及其同事从一名29岁的患有广泛、快速进展性恶性黑色素瘤的白人男性患者的胸导管中分离建立的。SK-MEL-1细胞可产生黑色素,电镜检测发现SK-MEL-1细胞中色素颗粒与自身合成和吞噬作用相关。在63%的恶性黑色素瘤患者和10%其他疾病患者体内发现了针对SK-MEL-1细胞的抗体。 |
| 年龄(性别) | 男性;29岁 |
| 组织来源 | 恶性黑色素瘤;皮肤;源自转移部位:淋巴系统 |
| 细胞类型 | 肿瘤细胞 |
| 肿瘤类型 | 黑色素瘤细胞 |
| 生物安全等级 | BSL-1 |
| 倍增时间 | ~100 hours |
| 致瘤性 | Yes, in nude mice; forms pigmented malignant melanomas; also forms tumors in the cheek pouch of cortisone treated hamsters. |
| 抗原表达情况 | Blood Type A; Rh+ |
| 保藏机构 | ATCC; HTB-67 DSMZ; ACC-303 |
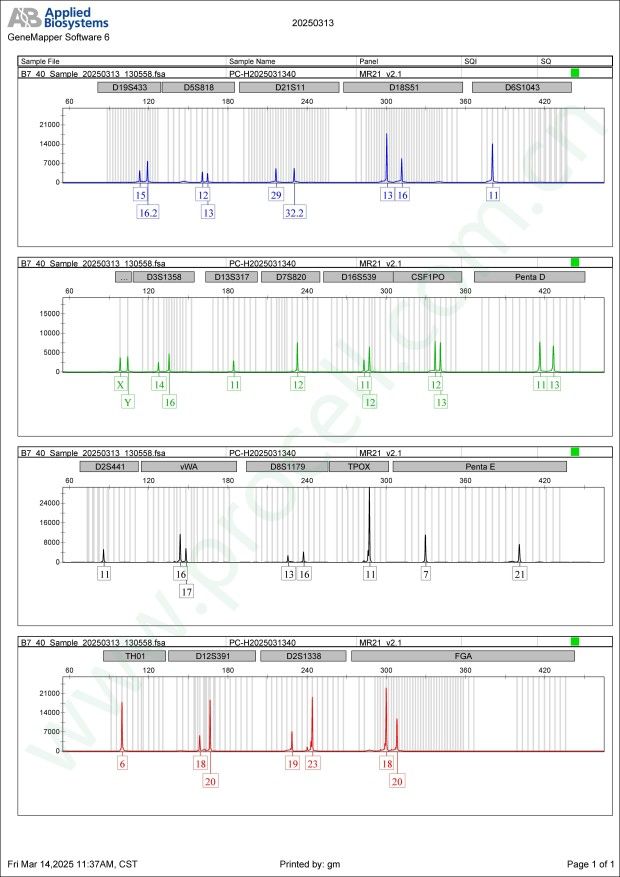
STR鉴定
-
STR位点信息
Amelogenin X,Y CSF1PO 12,13 D2S1338 19,23 D3S1358 14,16 D5S818 12,13 D7S820 12 D8S1179 13,16 D13S317 11 D16S539 11,12 D18S51 13,16 D19S433 15,16.2 D21S11 29,32.2 FGA 18,20 PentaD 11,13 PentaE 7,21 TH01 6 TPOX 11 vWA 16,17 D6S1043 11 D12S391 18,20 D2S441 11 -
STR鉴定图
-
参考文献
-
RNF144A-AS1 stabilizes TAF15 and promotes malignant biological behaviors of skin cutaneous melanoma (2024-06-15)
期刊:MOLECULAR AND CELLULAR BIOCHEMISTRY
DOI:10.1007/s11010-024-05045-6
影响因子 :3.5
引用产品: 特级胎牛血清 , SK-MEL-28 细胞 , HFF-1 细胞 , A875 [A-875] 细胞 , A-375 细胞 , SK-MEL-1 细胞 , 青霉素-链霉素溶液(双抗),100×
-
Anti-proliferative and pro-apoptotic effects of curcumin on skin cutaneous melanoma: Bioinformatics analysis and in vitro experimental studies. (2022-09-12)
期刊:Frontiers in Genetics
影响因子 :4.8
引用产品: SK-MEL-1 细胞
-
USP22 deficiency in melanoma mediates resistance to T?cells through IFNγ-JAK1-STAT1 signal axis (2021-02-15)
期刊:Molecular Therapy
DOI:10.1016/j.ymthe.2021.02.018
影响因子 :12.4
引用产品: A875 [A-875] 细胞 , SK-MEL-1 细胞
-
PURPL represses autophagic cell death to promote cutaneous melanoma by modulating ULK1 phosphorylation (2021-11-10)
期刊:Cell Death & Disease
DOI:10.1038/s41419-021-04362-8
影响因子 :9.0
引用产品: SK-MEL-1 细胞
FAQs
Q:为什么我看的文献里的细胞培养条件和你们官网的培养条件不一样呢?
A:部分细胞是会出现多种培养条件的,我们公司优先选择引种来源的培养条件以及建系者所用培养条件,出现差异的原因是不同实验室在保藏过程中更改了细胞的培养条件,为了避免细胞突然更换培养条件后不适应,建议您优先使用厂家推荐的培养条件培养。
Q:冻存细胞运输与常温细胞运输相比有什么区别?
A:发货有两种形式,常温或者冻存都可以的,常温就是货期一周左右(具体以购买当时销售报的货期为准),我们培养好一个T25瓶发货;冻存细胞如果有库存下单第二天能发货,细胞系冻存细胞担心客户复苏不成功所以赠送了一管,实际发货2管;冻存细胞发货是10公斤干冰及顺丰运输,所以冻存细胞需额外支付干冰及运输费。
Q:培养细胞的培养瓶可以重复利用吗?
A:一般不建议重复利用,特别是贴壁不牢固细胞,重复利用会导致吸附性变差,漂浮增多;一个T25瓶建议使用最多不超过3次,其次需要注意无菌操作,避免污染。
Q:冻存的细胞出现颜色不一致,有的红有的粉,对复苏会有影响吗?
A:这种情况容易在不同冻存批次间出现,与冻存细胞的密度、冻存液配方、温度导致pH变化等有关,偶尔有遇到这种情况,不是绝对性对细胞状态有影响,可以复苏看下。
Q:不同引种单位的同一株细胞,RRID都是一样的吗?
A:是的,同一个细胞系只有一个RRID。
产品资料


识别码示意图