产品中心Cell Resources
联系我们CONTACT US
 400-999-210024小时服务热线
400-999-210024小时服务热线
产品概述
| 名称 | HBZY-1 (大鼠肾小球系膜细胞) (种属鉴定正确) |
| 别称 | HBZY 1; HBZY1 |
| 种属 | 大鼠 |
| 生长特性 | 贴壁细胞 |
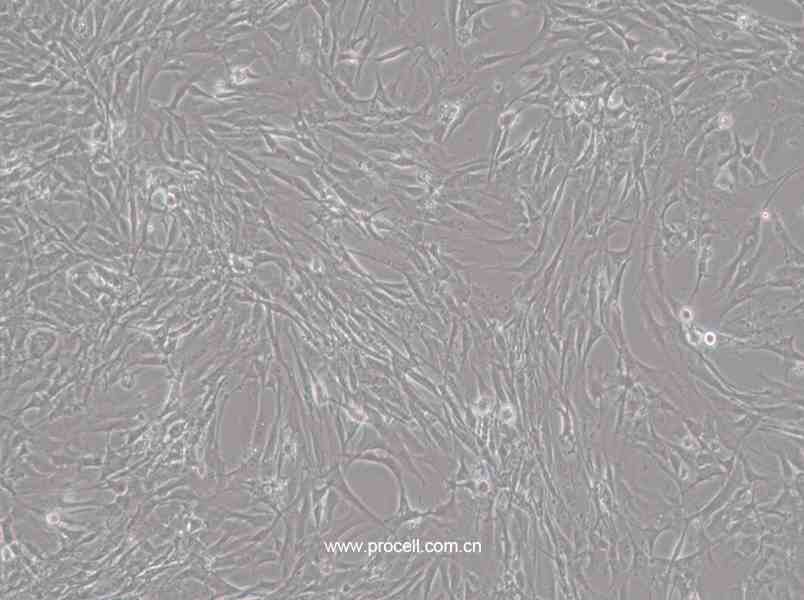
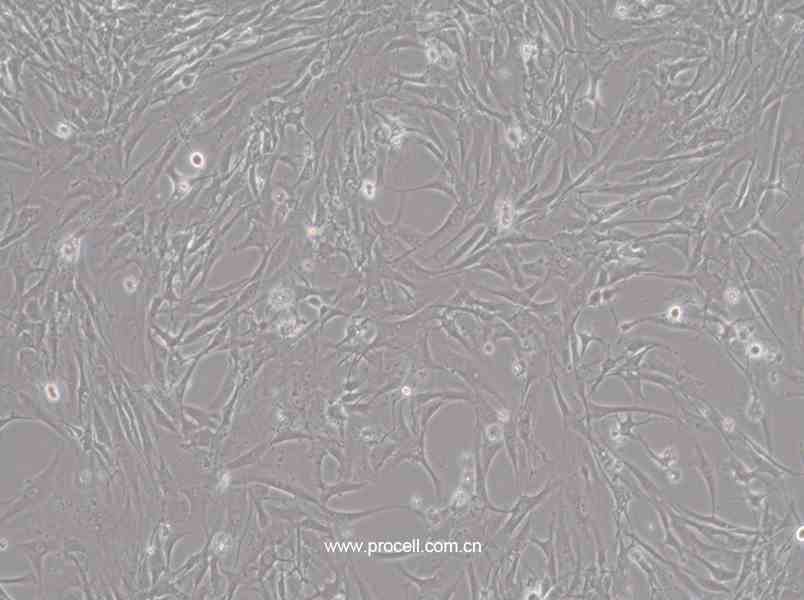
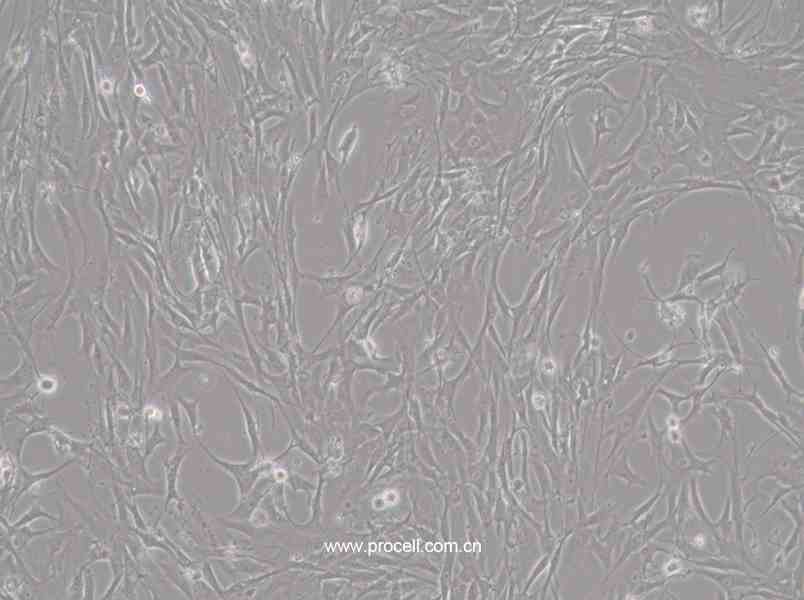
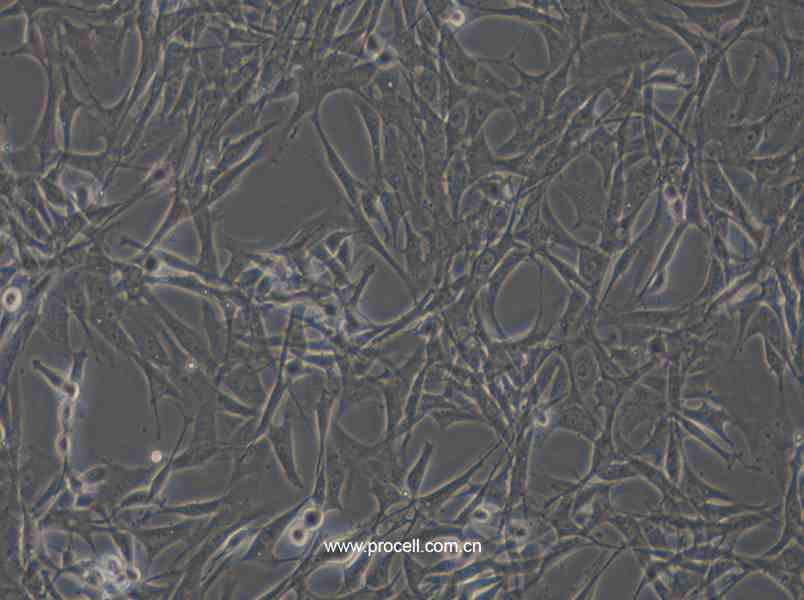
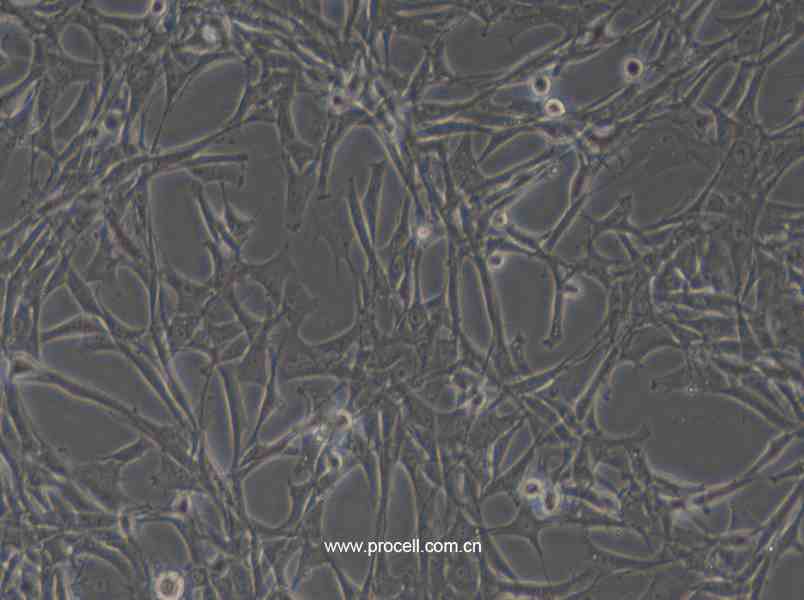
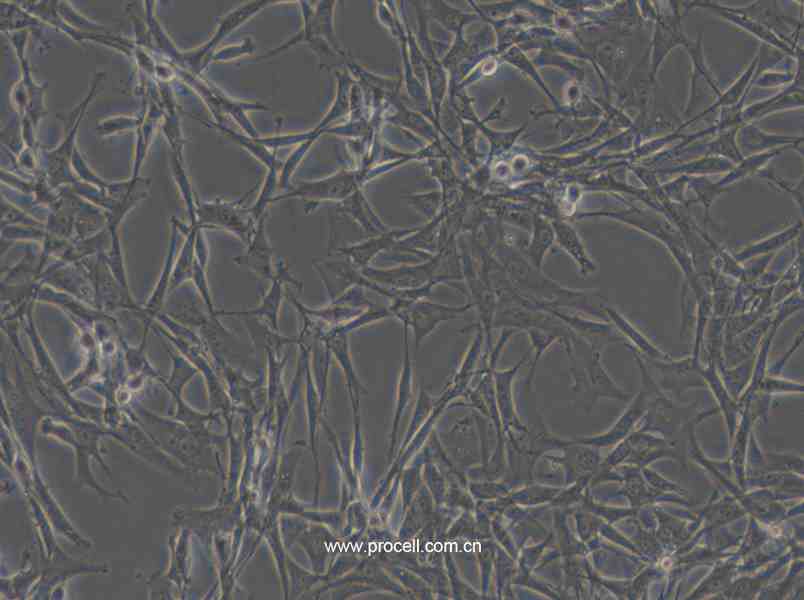
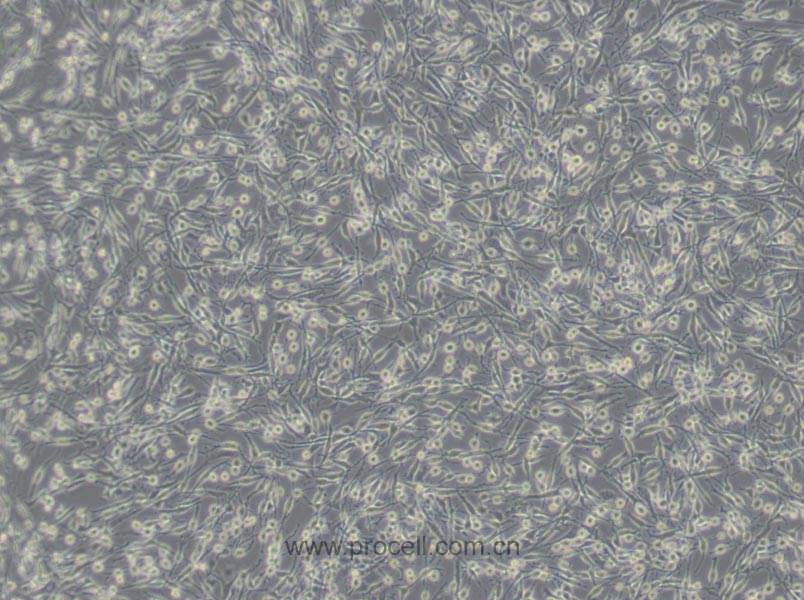
| 细胞形态 | 上皮细胞样 |
| 冻存条件 | 冻存液:55% 基础培养基+40%FBS+5%DMSO 温度:液氮 |
| 培养方案A(默认) |
培养条件:
气相:空气,95%;CO2,5%, 温度:37℃
|
| 推荐传代比例 | 1:2-1:4 |
| 推荐换液频率 | 2-3次/周 |
| 背景描述 | HBZY-1细胞是大鼠肾小球系膜细胞,贴壁生长;HBZY-1细胞常用于肾病发生机理的临床研究,也可用于构建动物摸型。 |
| 细胞类型 | 自发永生化细胞 |
| 生物安全等级 | BSL-1 |
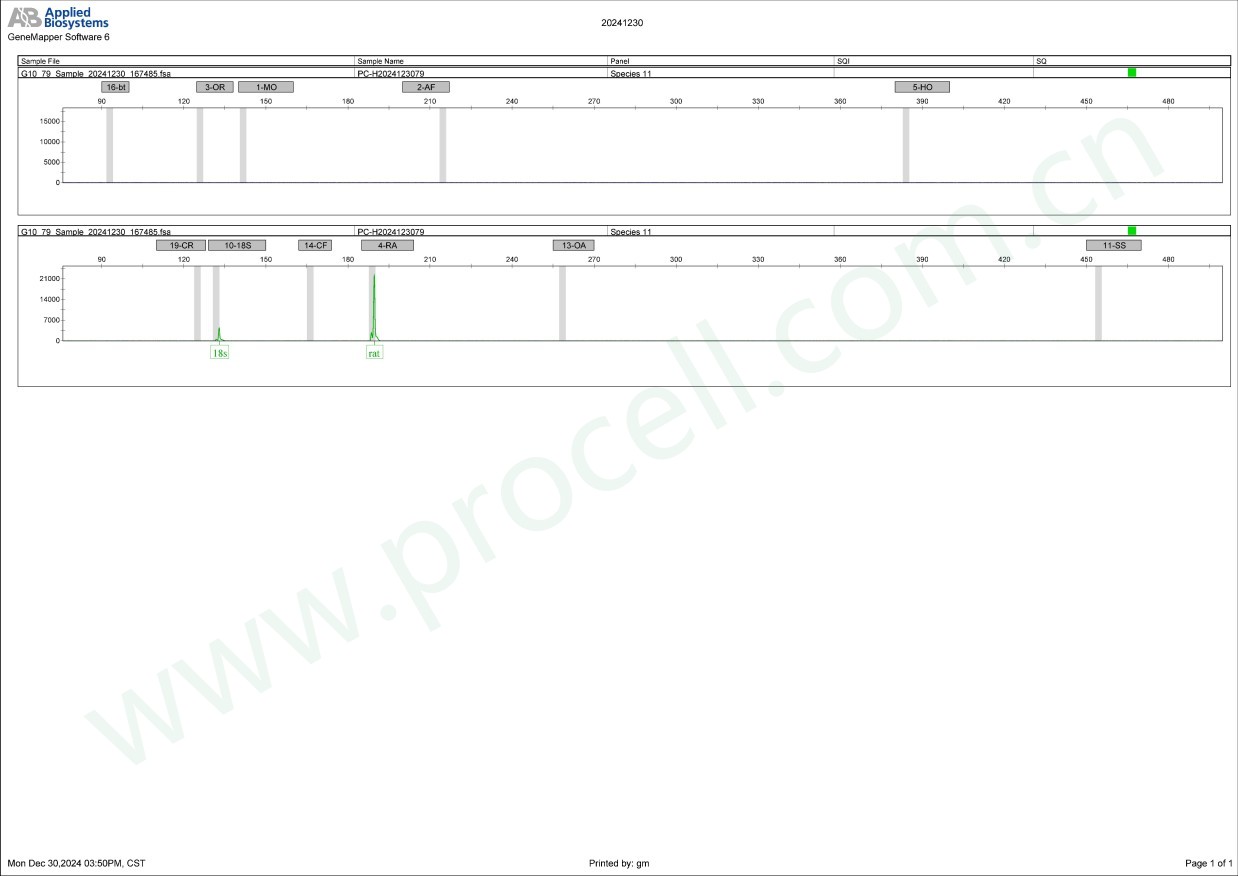
种属鉴定
-
种属鉴定图
-
参考文献
-
Discovery of the novel celastrol-based PROTACs for the treatment of non-small cell lung cancer (2025-02-18)
期刊:MOLECULAR DIVERSITY
DOI:10.1007/s11030-025-11140-7
影响因子 :3.9
引用产品: Annexin V-FITC/PI荧光双染细胞凋亡检测试剂盒 , NCI-H358 细胞 , NCI-H1975 细胞 , SW620 细胞 , MCF7 [MCF-7] 细胞 , HBZY-1 细胞
-
Plantaginis Semen ameliorates diabetic kidney disease via targeting the sphingosine kinase 1/sphingosine-1-phosphate pathway (2024-04-25)
期刊:JOURNAL OF ETHNOPHARMACOLOGY
影响因子 :4.8
引用产品: HBZY-1 细胞
-
Utilizing molecular docking and cell validation to explore the potential mechanisms of lupenone attenuating the inflammatory response via NF‐κB pathway (2024-01-05)
期刊:Scientific Reports
DOI:10.1038/s41598-024-51150-3
影响因子 :4.6
引用产品: HBZY-1 细胞
-
Excess iron accumulation mediated senescence in diabetic kidney injury (2024-03-14)
期刊:JOURNAL OF BIOCHEMICAL AND MOLECULAR TOXICOLOGY
影响因子 :3.6
-
A novel lncRNA TCONS_00071187 upregulated by activated GSK3β promotes high glucose-induced mesangial cell proliferation in the diabetic nephropathy (2024-01-31)
期刊:CELLULAR AND MOLECULAR BIOLOGY
影响因子 :1.5
引用产品: HBZY-1 细胞
-
Aptamer-assisted two-point immobilized agonist-bound angiotensin II type 1 receptor for a second-site modulator discovery (2022-10-14)
期刊:iScience
DOI:10.1016/j.isci.2022.105361
影响因子 :6.1
引用产品: HBZY-1 细胞
-
Echinacea polysaccharide attenuates lipopolysaccharide?induced acute kidney injury via inhibiting inflammation, oxidative stress and the MAPK signaling pathway (2021-01-01)
期刊:International Journal Of Molecular Medicine
影响因子 :5.4
引用产品: HBZY-1 细胞
FAQs
Q:{{item.question}}
A:
产品资料


识别码示意图





![LLC-WRC 256 [Walker 256] (大鼠腹水癌细胞) (种属鉴定正确)](/Public/upfile/pic/xbx/CL-0377-1.jpg)

































