产品中心Cell Resources
联系我们CONTACT US
 400-999-210024小时服务热线
400-999-210024小时服务热线
产品概述
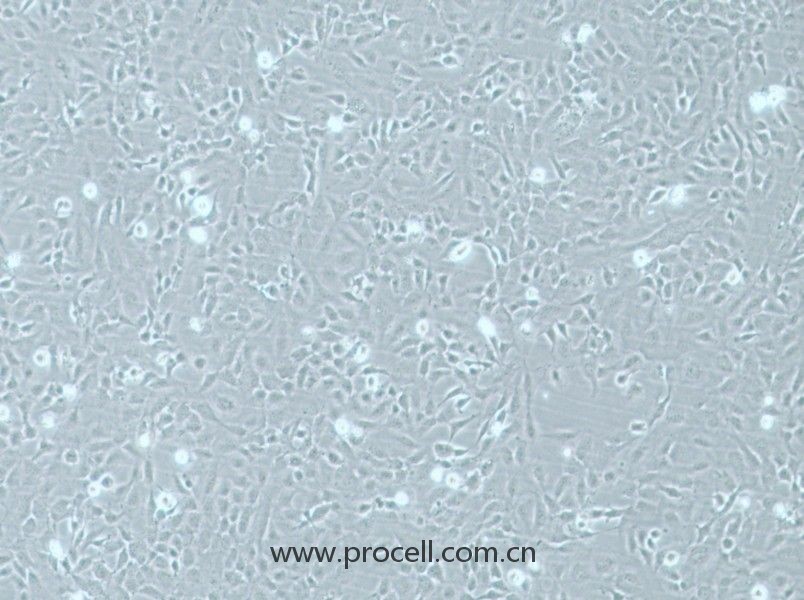
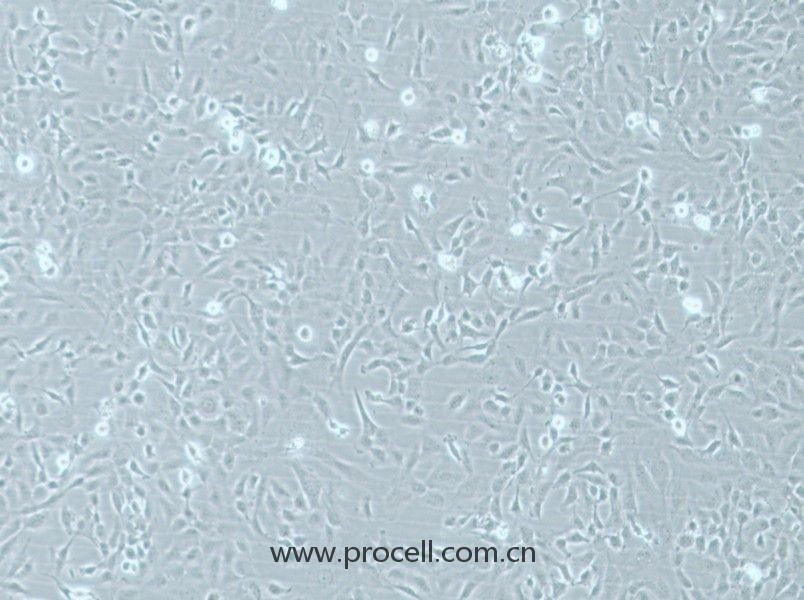
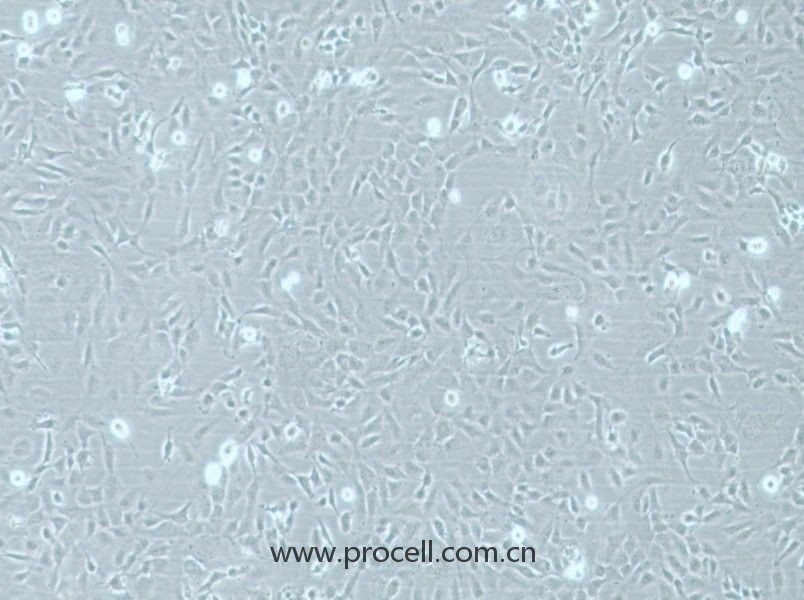
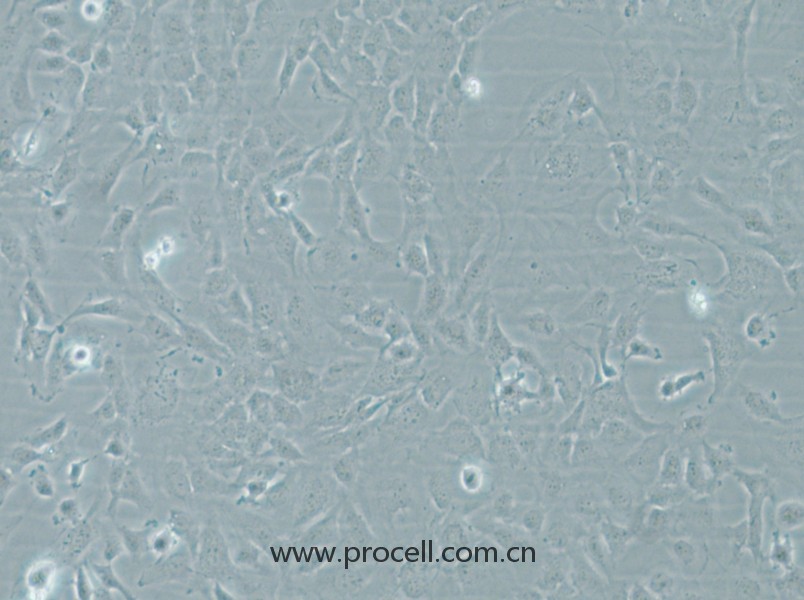
| 名称 | HMEC-1 (人微血管内皮细胞) (STR鉴定正确) |
| 别称 | Hmec-1; HMEC1; CDC/EU.HMEC-1; Human Microvascular Endothelial Cell line-1 |
| 种属 | 人 |
| 生长特性 | 贴壁细胞 |
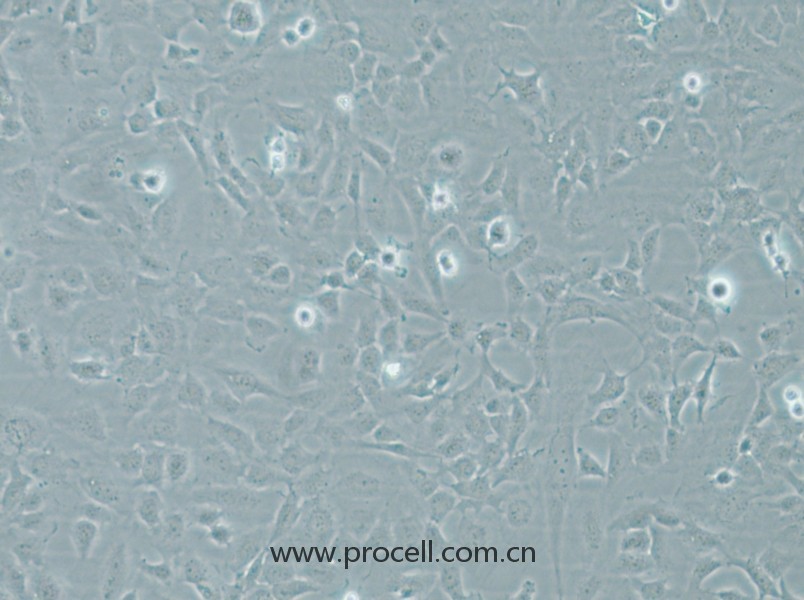
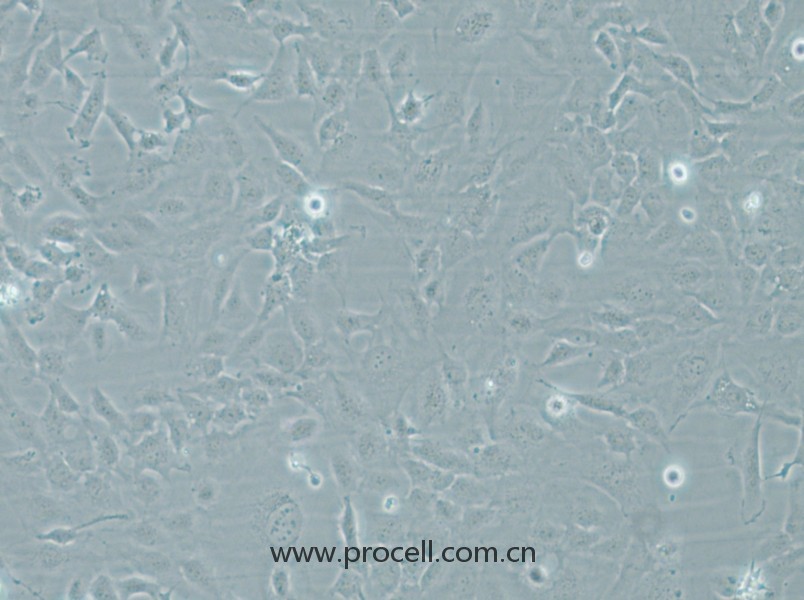
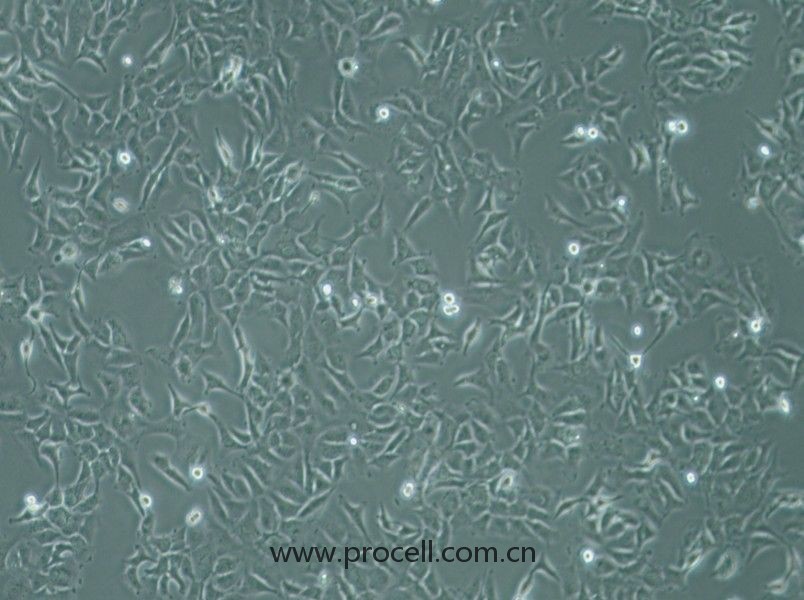
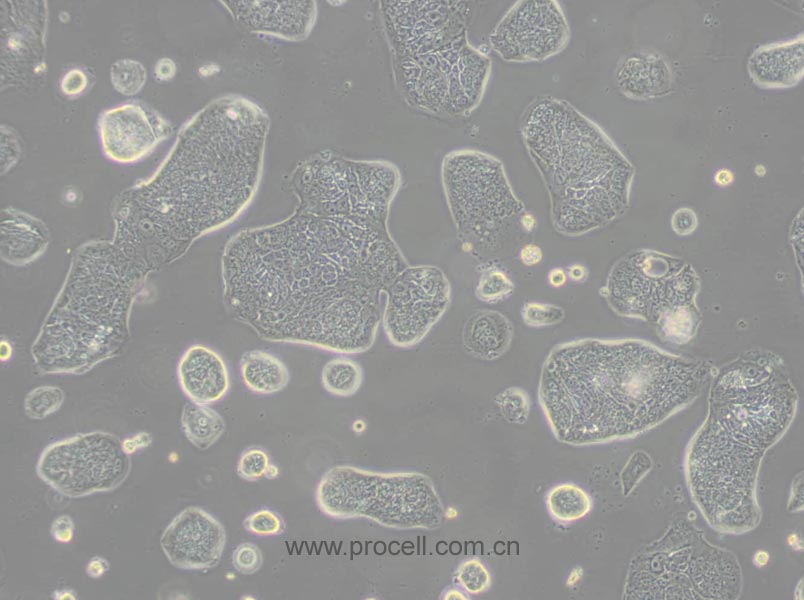
| 细胞形态 | 血管内皮类 |
| 冻存条件 | 冻存液:55% 基础培养基+40%FBS+5%DMSO 温度:液氮 |
| 培养方案A(默认) |
培养条件:
气相:空气,95%;CO2,5%, 温度:37℃
|
| 推荐传代比例 | 1:2-1:3 |
| 推荐换液频率 | 2-3次/周 |
| 背景描述 | HMEC-1是一种从男性患者包皮内皮中分离出来的内皮样细胞。该细胞系可用于心血管疾病的研究。HMEC-1细胞是从一位男性患者包皮中分离出的微血管内皮细胞,后经pSVT载体转染后,显示出保留了很多内皮细胞的特性,且通过连续传代获得的永生化细胞株。作为永生化细胞株,HMEC-1细胞是人类内皮微血管细胞的持续可再生来源之一,也可用于构建人真皮微血管内皮细胞体外模型,用于许多研究。 细胞可应用于血管生成、白细胞运输、伤口愈合、炎症、循环、肿瘤生长和转移。癌症研究,内皮功能,细胞运输,表面分子相互作用,药物筛选,制药和化妆品行业的毒理学研究。 |
| 年龄(性别) | 男性;新生儿 |
| 组织来源 | 真皮;微血管内皮 |
| 细胞类型 | 转化细胞系 |
| 生物安全等级 | BSL-2 |
| 倍增时间 | ~48 hours |
| 保藏机构 | ATCC; CRL-3243 |
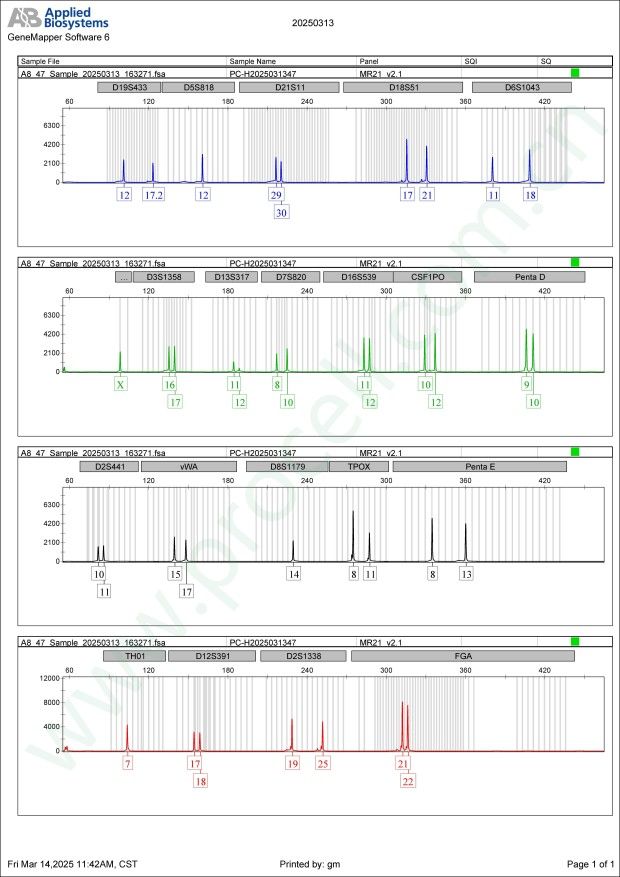
STR鉴定
-
STR位点信息
Amelogenin X CSF1PO 10,12 D2S1338 19,25 D3S1358 16,17 D5S818 12 D7S820 8,10 D8S1179 14 D13S317 11,12 D16S539 11,12 D18S51 17,21 D19S433 12,17.2 D21S11 29,30 FGA 21,22 PentaD 9,10 PentaE 8,13 TH01 7 TPOX 8,11 vWA 15,17 D6S1043 11,18 D12S391 17,18 D2S441 10,11 -
STR鉴定图
-
参考文献
-
ZBTB6 promotes breast cancer progression by inhibiting ARHGAP6 transcription and modulating the STAT3 signaling pathway (2025-03-25)
期刊:Journal of Translational Medicine
DOI:10.1186/s12967-025-06364-y
影响因子 :6.1
引用产品: HMEC-1 细胞 , BT-747 细胞 , T-47D 细胞 , MCF7 [MCF-7] 细胞
-
Selenium–Chondroitin Sulfate Nanoparticles Inhibit Angiogenesis by Regulating the VEGFR2-Mediated PI3K/Akt Pathway (2025-01-02)
期刊:Marine Drugs
影响因子 :4.9
引用产品: HMEC-1 细胞 , HMEC-1细胞专用培养基 , 特级胎牛血清
-
Treponema pallidum protein Tp0136 promotes angiogenesis to facilitate the dissemination of Treponema pallidum (2024-07-19)
期刊:Emerging Microbes & Infections
DOI:10.1080/22221751.2024.2382236
影响因子 :8.4
引用产品: HMEC-1 细胞 , HMEC-1细胞专用培养基
-
Structure-Activity Relationship Study of New Carbazole Sulfonamide Derivatives as Anticancer Agents with Dual-target Mechanism (2024-05-16)
期刊:EUROPEAN JOURNAL OF MEDICINAL CHEMISTRY
DOI:10.1016/j.ejmech.2024.116509
影响因子 :6.7
-
Microfibril-AssociatedGlycoprotein-2 Promoted Fracture Healing via Integrin αvβ3/PTK2/AKT Signaling (2023-03-17)
期刊:LABORATORY INVESTIGATION
DOI:10.1016/j.labinv.2023.100121
影响因子 :5.0
引用产品: HMEC-1 细胞
-
Overexpression and potential roles of midkine via regulation of vascular endothelial growth factor A in psoriasis (2023-05-23)
期刊:EXPERIMENTAL DERMATOLOGY
影响因子 :3.6
引用产品: HMEC-1 细胞 , lipopolysaccharide A
-
KLF10 knockdown negatively regulates CTRP3 to improve OGD/R-induced brain microvascular endothelial cell injury and barrier dysfunction through Nrf2/HO-1 signaling pathway (2023-05-10)
期刊:TISSUE & CELL
DOI:10.1016/j.tice.2023.102106
影响因子 :2.6
引用产品: HMEC-1 细胞
-
Photocatalytic glucose depletion and hydrogen generation for diabetic wound healing (2022-09-27)
期刊:Nature Communications
DOI:10.1038/s41467-022-33475-7
影响因子 :17.7
引用产品: Hacat 细胞 , 人真皮成纤维细胞 , HMEC-1 细胞 , HMEC-1细胞专用培养基
-
Two-Dimensional Mg2Si Nanosheet-Enabled Sustained Hydrogen Generation for Improved Repair and Regeneration of Deeply Burned Skin (2022-12-22)
期刊:Advanced Healthcare Materials
影响因子 :11.1
引用产品: Hacat 细胞 , 人真皮成纤维细胞 , HMEC-1 细胞 , HMEC-1细胞专用培养基
-
LncRNA SNHG12 alleviates hypertensive vascular endothelial injury through miR‐25‐3p/SIRT6 pathway (2021-01-19)
期刊:Journal Of Leukocyte Biology
影响因子 :5.5
引用产品: MCDB 131 (不含L-谷氨酰胺) 培养基 , HMEC-1 细胞
-
An Integrated Smart Sensor Dressing for Real-Time Wound Microenvironment Monitoring and Promoting Angiogenesis and Wound Healing (2021-08-06)
期刊:Frontiers in Cell and Developmental Biology
影响因子 :5.5
引用产品: HMEC-1 细胞
-
Hypoxic tubular epithelial cells regulate the angiogenesis of HMEC-1 cells via mediation of Rab7/MMP-2 axis (2021-10-25)
期刊:Aging-US
影响因子 :5.2
引用产品: HMEC-1 细胞
-
Human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells prevent glucocorticoid-induced osteonecrosis of the femoral head by promoting angiogenesis (2021-09-27)
期刊:Journal of Plastic Surgery and Hand Surgery
DOI:10.1080/2000656X.2021.1981352
影响因子 :1.3
引用产品: HMEC-1 细胞
-
The potential of Diosgenin in treating psoriasis: Studies from HaCaT keratinocytes and imiquimod-induced murine model (2019-11-29)
期刊:Life Sciences
影响因子 :6.1
FAQs
Q:{{item.question}}
A:
产品资料


识别码示意图