产品中心Cell Resources
联系我们CONTACT US
 400-999-210024小时服务热线
400-999-210024小时服务热线
产品概述
| 名称 | HMC3 (人小胶质细胞) (STR鉴定正确) |
| 别称 | Human Microglia Clone 3 |
| 种属 | 人 |
| 生长特性 | 贴壁细胞 |
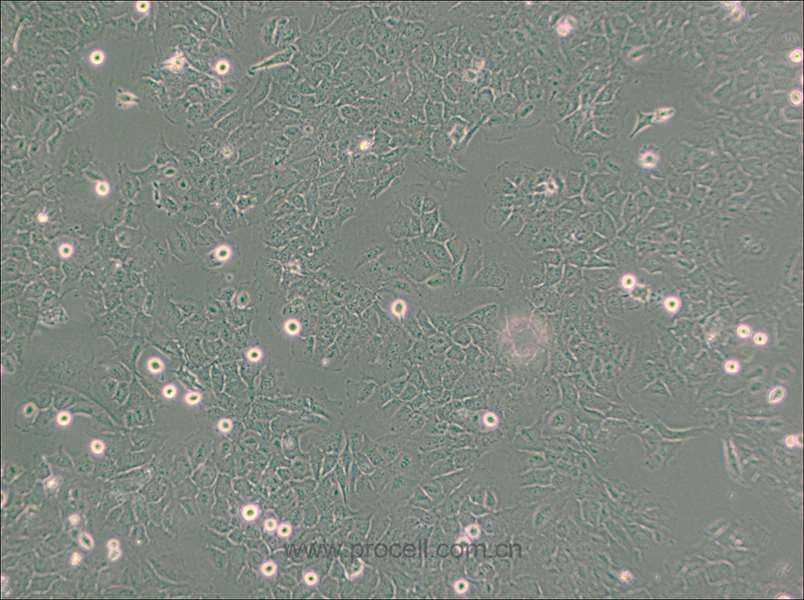
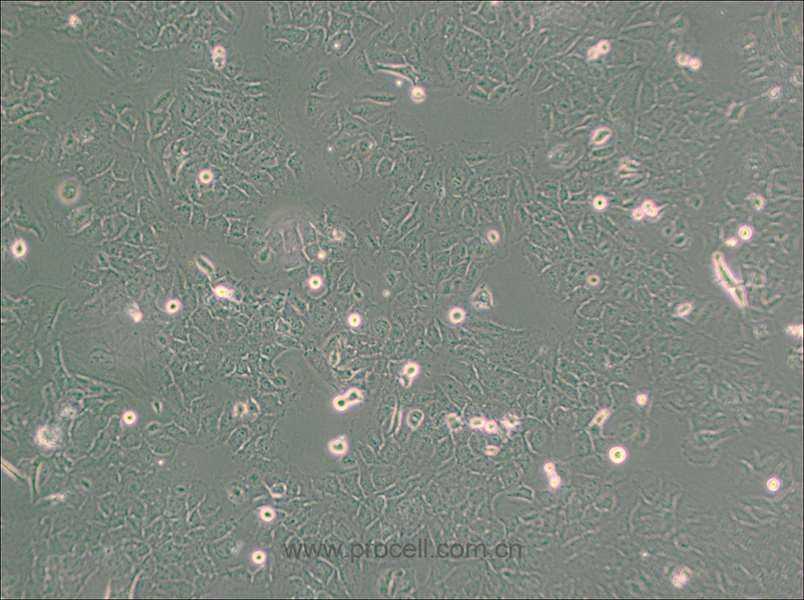
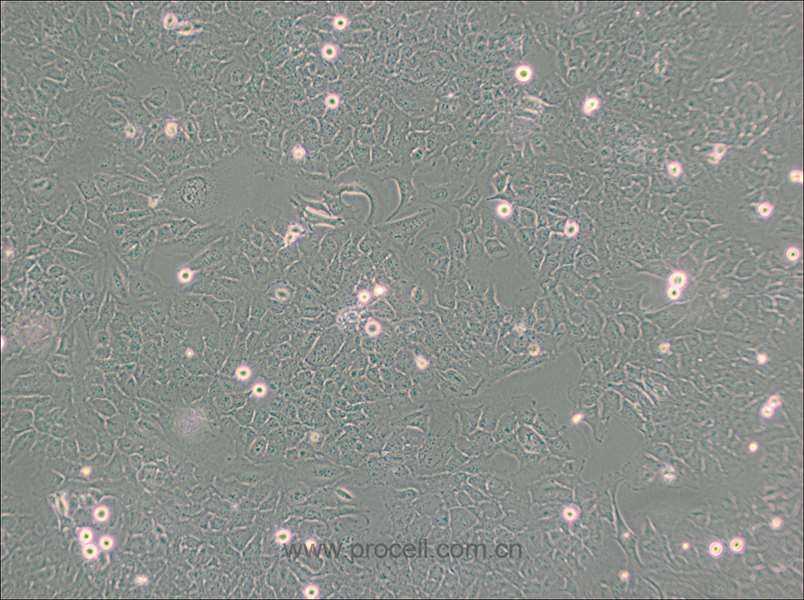
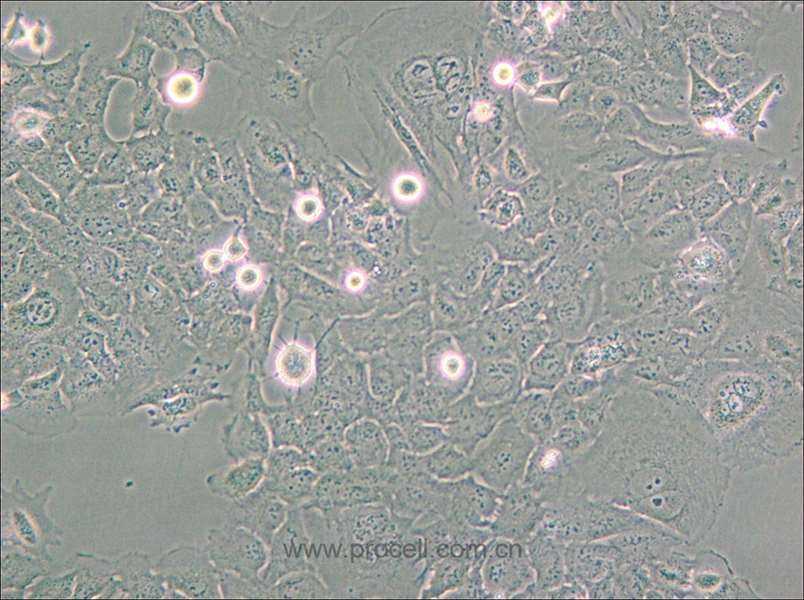
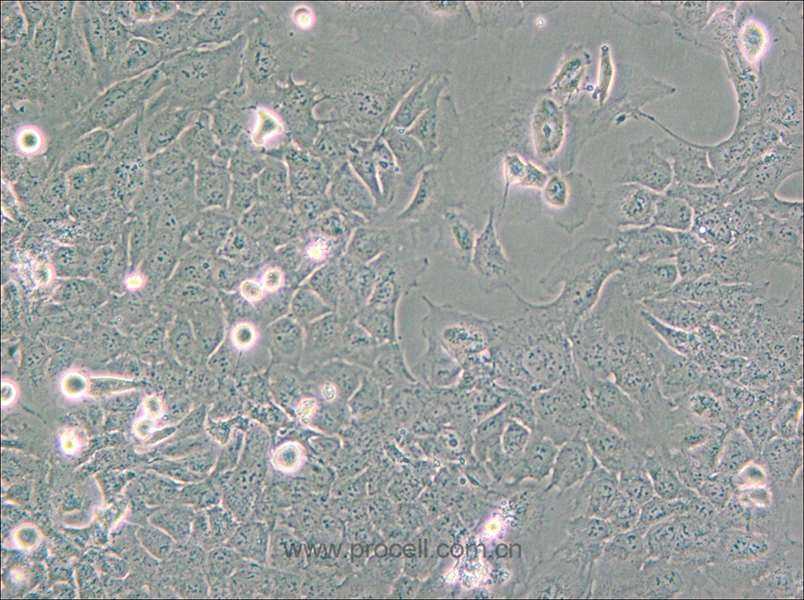
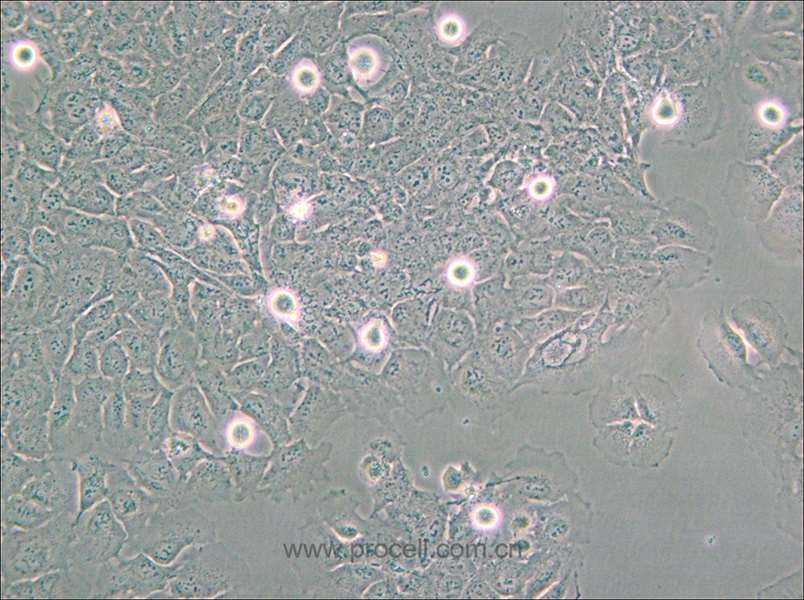
| 细胞形态 | 上皮细胞样 |
| 冻存条件 | 冻存液:55% 基础培养基+40%FBS+5%DMSO 温度:液氮 |
| 培养方案A(默认) |
生长培养基:
培养条件:
气相:空气,95%;CO2,5%, 温度:37℃
|
| 推荐传代比例 | 1:3-1:8 |
| 推荐换液频率 | 2-3次/周 |
| 背景描述 | The HMC3 cell line was established through SV40-dependent immortalization of a human fetal brain-derived primary microglia culture. |
| 年龄(性别) | 胚胎 |
| 组织来源 | 脑组织 |
| 细胞类型 | 转化细胞系 |
| 生物安全等级 | BSL-2 |
| 保藏机构 | ATCC; CRL-3304 |
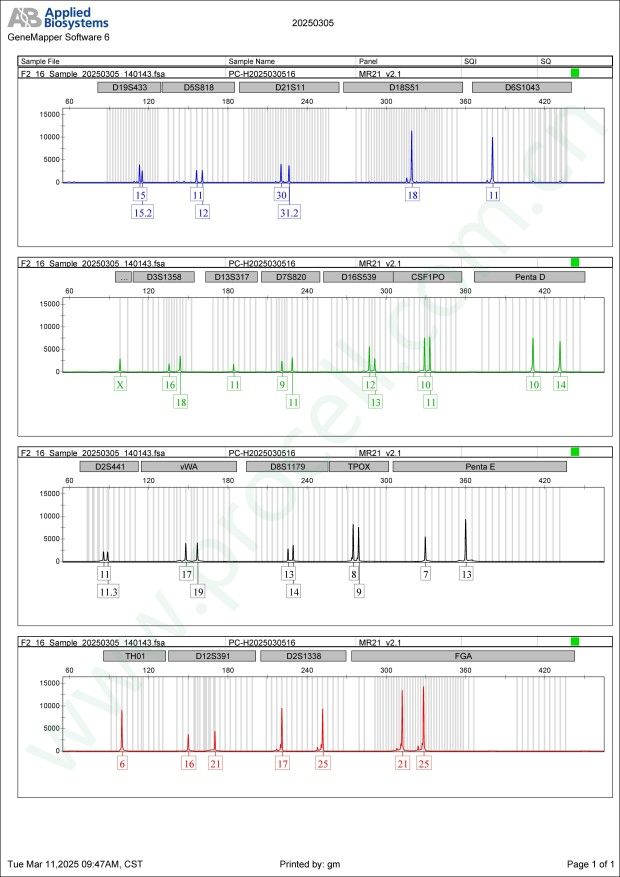
STR鉴定
-
STR位点信息
Amelogenin X CSF1PO 10,11 D2S1338 17,25 D3S1358 16,18 D5S818 11,12 D7S820 9,11 D8S1179 13,14 D13S317 11 D16S539 12,13 D18S51 18 D19S433 15,15.2 D21S11 30,31.2 FGA 21,25 PentaD 10,14 PentaE 7,13 TH01 6 TPOX 8,9 vWA 17,19 D6S1043 11 D12S391 16,21 D2S441 11,11.3 -
STR鉴定图
-
参考文献
-
Astrocyte-Derived Interleukin 11 Modulates Astrocyte–Microglia Crosstalk via Nuclear Factor-κB Signaling Pathway in Sepsis-Associated Encephalopathy (2025-01-30)
期刊:Research
影响因子 :8.5
引用产品: U251 细胞 , HMC3 细胞 , MEM(含NEAA) 培养基
-
Trace component fishing strategy based on offline two-dimensional liquid chromatography combined with PRDX3-surface plasmon resonance for Uncaria alkaloids (2025-02-20)
期刊:Journal of Pharmaceutical Analysis
DOI:10.1016/j.jpha.2025.101244
影响因子 :6.1
引用产品: HMC3 细胞
-
From Gene Discovery to Stroke Risk: C5orf24's Pivotal Role Uncovered (2025-03-05)
期刊:MOLECULAR NEUROBIOLOGY
DOI:10.1007/s12035-025-04802-y
影响因子 :4.6
引用产品: HMC3 细胞 , 特级胎牛血清 , DMEM高糖 培养基
-
Developing and validating a prognostic disulfidptosis-related signature for glioblastoma: predicting radioresistance and synergestic effect with immunotherapy (2025-03-18)
期刊:JOURNAL OF CANCER RESEARCH AND CLINICAL ONCOLOGY
DOI:10.1007/s00432-025-06159-0
影响因子 :2.7
引用产品: LN229 [LN-229; LNT-229] 细胞 , U-87 MG 细胞 , T98G 细胞 , HMC3 细胞
-
Berberine Exerts Neuroprotective Effects in Alzheimer's Disease by Switching Microglia M1/M2 Polarization Through PI3K-AKT Signaling (2025-03-24)
期刊:PHYSIOLOGICAL RESEARCH
DOI:PMID:40126149
影响因子 :1.9
引用产品: HMC3 细胞 , SH-SY5Y [SHSY-5Y] 细胞 , DMEM/F12 培养基
-
Super-enhancer-driven LIF promotes the mesenchymal transition in glioblastoma by activating ITGB2 signaling feedback in microglia (2024-03-30)
期刊:NEURO-ONCOLOGY
影响因子 :15.9
引用产品: LN229 [LN-229; LNT-229] 细胞 , SF126 细胞 , U-87 MG 细胞 , HMC3 细胞 , BV2 细胞
-
Circular RNA circ_0061183 regulates microglial polarization induced by airborne ultrafine particles in HMC3 cells via sponging miR-98-5p (2024-11-29)
期刊:JOURNAL OF HAZARDOUS MATERIALS
DOI:10.1016/j.jhazmat.2024.136719
影响因子 :12.2
-
The dual role of POSTN in maintaining glioblastoma stem cells and the immunosuppressive phenotype of microglia in glioblastoma (2024-09-04)
期刊:JOURNAL OF EXPERIMENTAL & CLINICAL CANCER RESEARCH
DOI:10.1186/s13046-024-03175-9
影响因子 :11.4
-
Polyvinylpyrrolidone-curcumin nanoparticles with immune regulatory and metabolism regulatory effects for the treatment of experimental autoimmune uveitis (2024-06-28)
期刊:JOURNAL OF CONTROLLED RELEASE
DOI:10.1016/j.jconrel.2024.06.047
影响因子 :10.5
引用产品: ARPE-19 细胞 , HMC3细胞专用培养基 , HMC3 细胞
-
Understanding the molecular pathway of triclosan-induced ADHD-like behaviour: Involvement of the hnRNPA1-PKM2-STAT3 feedback loop (2024-08-17)
期刊:ENVIRONMENT INTERNATIONAL
DOI:10.1016/j.envint.2024.108966
影响因子 :10.3
引用产品: HMC3 细胞 , 青霉素-链霉素溶液(双抗),100× , DMEM高糖 培养基 , 特级胎牛血清
-
Ganglion cell-derived LysoPS induces retinal neovascularisation by activating the microglial GPR34-PI3K-AKT-NINJ1 axis (2024-10-28)
期刊:Journal of Neuroinflammation
DOI:10.1186/s12974-024-03265-7
影响因子 :9.3
引用产品: HMC3 细胞
-
Remifentanil-induced inflammation in microglial cells: Activation of the PAK4-mediated NF-κB/NLRP3 pathway and onset of hyperalgesia (2024-09-24)
期刊:BRAIN BEHAVIOR AND IMMUNITY
影响因子 :8.8
引用产品: HMC3 细胞 , 青霉素-链霉素溶液(双抗),100×
-
Egln3 expression in microglia enhances the neuroinflammatory responses in Alzheimer’s disease (2024-12-17)
期刊:BRAIN BEHAVIOR AND IMMUNITY
影响因子 :8.8
-
SIRPB1 regulates inflammatory factor expression in the glioma microenvironment via SYK: functional and bioinformatics insights (2024-04-09)
期刊:Journal of Translational Medicine
DOI:10.1186/s12967-024-05149-z
影响因子 :7.4
-
PM2.5 exposure upregulates pro-inflammatory protein expression in human microglial cells via oxidant stress and TLR4/NF-κB pathway (2024-04-23)
期刊:ECOTOXICOLOGY AND ENVIRONMENTAL SAFETY
DOI:10.1016/j.ecoenv.2024.116386
影响因子 :6.8
引用产品: HMC3 细胞
-
Mesenchymal stem cell-derived small extracellular vesicles enhance the therapeutic effect of retinal progenitor cells in retinal degenerative disease rats (2024-07-29)
期刊:Neural Regeneration Research
DOI:10.4103/NRR.NRR-D-23-02108
影响因子 :5.9
引用产品: HMC3 细胞
-
Microglia-endothelial cross-talk regulates diabetes-induced retinal vascular dysfunction through remodeling inflammatory microenvironment (2024-02-06)
期刊:iScience
DOI:10.1016/j.isci.2024.109145
影响因子 :5.8
引用产品: HMC3 细胞
-
Hypoxia-induced activation of HIF-1alpha/IL-1beta axis in microglia promotes glioma progression via NF-κB-mediated upregulation of heparanase expression (2024-06-11)
期刊:Biology Direct
DOI:10.1186/s13062-024-00487-w
影响因子 :5.7
引用产品: U251 细胞 , U-87 MG 细胞 , HMC3 细胞
-
A New Modulator of Neuroinflammation in Diabetic Retinopathy: USP25 (2024-03-04)
期刊:INFLAMMATION
DOI:10.1007/s10753-024-01991-x
影响因子 :5.1
-
Facilitating microglia M2 polarization alleviates p-Synephrine-induced depressive-like behaviours in CSDS mice via the 5-HT6R-FYN-ERK1/2 pathway (2024-12-31)
期刊:INTERNATIONAL IMMUNOPHARMACOLOGY
DOI:10.1016/j.intimp.2024.113926
影响因子 :4.8
引用产品: HMC3 细胞 , HMC3细胞专用培养基
-
MST1/2 exerts a pivotal role in inducing neuroinflammation and Coxsackievirus-A10 replication by interacting with innate immunity (2024-04-19)
期刊:Virology Journal
DOI:10.1186/s12985-024-02355-5
影响因子 :4.8
引用产品: HMC3 细胞
-
Unraveling the molecular mechanisms of Ace2-mediated post-COVID-19 cognitive dysfunction through systems genetics approach (2024-08-12)
期刊:EXPERIMENTAL NEUROLOGY
DOI:10.1016/j.expneurol.2024.114921
影响因子 :4.6
-
Nicotinamide N-oxide Inhibits Microglial Pyroptosis by Upregulating Mitophagy and Alleviates Neural Damage in Rats after TBI (2024-10-30)
期刊:INFLAMMATION
DOI:10.1007/s10753-024-02171-7
影响因子 :4.5
引用产品: HMC3 细胞
-
N-Salicyloyl Tryptamine Derivatives as Potent Neuroinflammation Inhibitors by Constraining Microglia Activation via a STAT3 Pathway (2024-06-12)
期刊:ACS Chemical Neuroscience
DOI:10.1021/acschemneuro.4c00060
影响因子 :4.1
引用产品: SH-SY5Y [SHSY-5Y] 细胞 , BV2 细胞 , HMC3 细胞
-
EP300 regulates the SLC16A1-AS1-AS1/TCF3 axis to promote lung cancer malignancies through the Wnt signaling pathway (2024-03-07)
期刊:Heliyon
DOI:10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e27727
影响因子 :3.4
-
Oxidized low-density lipoprotein changes the inflammatory status and metabolomics profiles in human and mouse macrophages and microglia (2024-03-29)
期刊:Heliyon
DOI:10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e28806
影响因子 :3.4
引用产品: BV2 细胞 , J774A.1 细胞 , HMC3 细胞 , THP-1 细胞
-
Estimates of Natural Frequencies for Nuclear Vibration, and an Assessment of the Feasibility of Selective Ultrasound Ablation of Cancer Cells (2024-10-11)
期刊:Journal of the Mechanical Behavior of Biomedical Materials
DOI:10.1016/j.jmbbm.2024.106778
影响因子 :3.3
引用产品: HMC3 细胞 , Ham's F-10 培养基 , MEM 培养基 , 人神经星形胶质细胞 , GH3 细胞 , 磷酸盐缓冲液(PBS) 1× , Ham's F-12K 培养基 , NSC-34 细胞 , U-87 MG 细胞 , MMQ 细胞 , BV2 (DMEM) 细胞 , GL261 细胞 , DMEM高糖 培养基
-
Identification of Disulfidptosis-Related Genes in Ischemic Stroke by Combining Single-Cell Sequencing, Machine Learning Algorithms, and In Vitro Experiments (2024-09-15)
期刊:NEUROMOLECULAR MEDICINE
DOI:10.1007/s12017-024-08804-2
影响因子 :3.3
引用产品: MEM(ATCC改良) 培养基 , HMC3 细胞
-
Severe hypoglycaemia-induced microglial inflammation damages microvascular endothelial cells, leading to retinal destruction (2024-08-26)
期刊:Diabetes & Vascular Disease Research
影响因子 :2.8
引用产品: HMC3 细胞
-
Jagged1-Notch1 Signaling Pathway Induces M1 Microglia to Disrupt the Barrier Function of Retinal Microvascular Endothelial Cells (2024-05-23)
期刊:CURRENT EYE RESEARCH
DOI:10.1080/02713683.2024.2357601
影响因子 :2.0
引用产品: HMC3 细胞 , DMEM低糖 培养基 , HMC3细胞专用培养基
-
Regulation of a novel circATP8B4/miR-31-5p/nestin ceRNA crosstalk in proliferation, motility, invasion and radiosensitivity of human glioma cells (2024-09-17)
期刊:JOURNAL OF RADIATION RESEARCH
影响因子 :1.9
引用产品: T98G 细胞 , HMC3 细胞 , U251 细胞 , A172 细胞 , LN229 [LN-229; LNT-229] 细胞
-
CHIT1-positive microglia drive motor neuron ageing in the primate spinal cord (2023-10-31)
期刊:NATURE
DOI:10.1038/s41586-023-06783-1
影响因子 :64.8
引用产品: HMC3 细胞
-
Blood–brain barrier injury and neuroinflammation induced by SARS-CoV-2 in a lung–brain microphysiological system (2023-06-22)
期刊:Nature Biomedical Engineering
DOI:10.1038/s41551-023-01054-w
影响因子 :28.1
引用产品: HULEC-5a 细胞 , HULEC-5a细胞专用培养基 , HMC3 细胞 , MEM (含NEAA) 培养基
-
Nanoplastic Stimulates the Amyloidogenesis of Parkinson's Alpha-Synuclein NACore (2023-11-21)
期刊:Small
影响因子 :13.3
引用产品: HMC3 细胞 , HMC3细胞专用培养基
-
Microglial aryl hydrocarbon receptor enhances phagocytic function via SYK and promotes remyelination in the cuprizone mouse model of demyelination (2023-03-25)
期刊:Journal of Neuroinflammation
DOI:10.1186/s12974-023-02764-3
影响因子 :9.3
引用产品: HMC3 细胞 , MEM完全培养基 (含10%FBS)
-
BAFF deficiency aggravated optic nerve crush-induced retinal ganglion cells damage by regulating apoptosis and neuroinflammation via NF-κB-IκBα signaling (2023-12-04)
期刊:INTERNATIONAL IMMUNOPHARMACOLOGY
DOI:10.1016/j.intimp.2023.111287
影响因子 :5.6
引用产品: HMC3 细胞
-
Parthenolide alleviates microglia‐mediated neuroinflammation via MAPK/TRIM31/NLRP3 signaling to ameliorate cognitive disorder (2023-05-12)
期刊:INTERNATIONAL IMMUNOPHARMACOLOGY
DOI:10.1016/j.intimp.2023.110287
影响因子 :5.6
-
α-Synuclein Induces Neuroinflammation Injury through the IL6ST-AS/STAT3/HIF-1α Axis (2023-01-11)
期刊:INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF MOLECULAR SCIENCES
影响因子 :5.6
引用产品: HMC3 细胞 , SH-SY5Y [SHSY-5Y] 细胞
-
Oncolytic Viral Therapy for Glioma by Recombinant Sindbis Virus (2023-09-27)
期刊:Cancers
影响因子 :5.2
引用产品: U-87 MG 细胞 , BV2 细胞 , HMC3 细胞 , U-118 MG 细胞 , C6 细胞 , GL261 细胞
-
Htr2b Promotes M1 Microglia Polarization and Neuroinflammation after Spinal Cord Injury via Inhibition of Neuregulin-1/ErbB Signaling (2023-09-25)
期刊:MOLECULAR NEUROBIOLOGY
DOI:10.1007/s12035-023-03656-6
影响因子 :5.1
-
LASSO-based screening for potential prognostic biomarkers associated with glioblastoma (2023-01-16)
期刊:Frontiers in Oncology
影响因子 :4.7
-
Daphnetin Improves Neuropathic Pain by Inhibiting the Expression of Chemokines and Inflammatory Factors in the Spinal Cord and Interfering with Glial Cell Polarization (2023-02-06)
期刊:Pharmaceuticals
影响因子 :4.6
-
Exploring the Therapeutic Effects of Multifunctional N-Salicylic Acid Tryptamine Derivative against Parkinson’s Disease (2023-07-28)
期刊:ACS Omega
影响因子 :4.1
引用产品: SH-SY5Y [SHSY-5Y] 细胞 , HMC3 细胞
-
Elevated LILRB1 expression predicts poor prognosis and is associated with tumor immune infiltration in patients with glioma (2023-05-04)
期刊:BMC CANCER
DOI:10.1186/s12885-023-10906-2
影响因子 :3.8
引用产品: HMC3 细胞
-
Triptolide improves Alzheimer's disease by regulating the NF?κB signaling pathway through the lncRNA NEAT1/microRNA 361?3p/TRAF2 axis (2023-08-01)
期刊:Experimental and Therapeutic Medicine
影响因子 :2.7
引用产品: HMC3 细胞
-
Microglia increase CEMIP expression and promote brain metastasis in breast cancer through the JAK2/STAT3 signaling pathway (2023-11-21)
期刊:Oncologie
DOI:10.1515/oncologie-2023-0312
影响因子 :0.9
引用产品: HMC3 细胞
-
Developmental exposure to chlorpyrifos causes neuroinflammation via necroptosis in mouse hippocampus and human microglial cell line (2022-09-23)
期刊:ENVIRONMENTAL POLLUTION
DOI:10.1016/j.envpol.2022.120217
影响因子 :10.0
引用产品: HMC3 细胞 , HMC3细胞专用培养基
-
lncRNA SND1-IT1 delivered via intracerebral hemorrhage-derived exosomes affect the growth of human microglia by regulating the miR-124-3p/MTF1 axis (2022-12-22)
期刊:JOURNAL OF CELLULAR PHYSIOLOGY
影响因子 :6.5
引用产品: HMC3 细胞
-
TMEM16F may be a new therapeutic target for Alzheimer’s disease (2022-08-02)
期刊:Neural Regeneration Research
影响因子 :6.1
引用产品: HMC3 细胞 , MEM (含NEAA) 培养基 , 特级胎牛血清 , DMEM低糖 (不含酚红) 培养基
-
Sevoflurane-induced POCD-associated exosomes delivered miR-584-5p regulates the growth of human microglia HMC3 cells through targeting BDNF (2022-11-30)
期刊:Aging-US
影响因子 :6.0
引用产品: HMC3 细胞
-
Malignant Melanoma-Derived Exosomes Induce Endothelial Damage and Glial Activation on a Human BBB Chip Model (2022-01-31)
期刊:Biosensors-Basel
影响因子 :5.7
引用产品: MEM(含NEAA) 培养基 , HMC3 细胞
-
Iron oxide nanoparticles loaded with paclitaxel inhibits glioblastoma by enhancing autophagy-dependent ferroptosis pathway (2022-03-09)
期刊:European Journal Of Pharmacology
DOI:10.1016/j.ejphar.2022.174860
影响因子 :5.0
引用产品: HMC3 细胞
-
LINC01088 promotes the growth and invasion of glioma cells through regulating small nuclear ribonucleoprotein polypeptide A transcription (2022-04-07)
期刊:Bioengineered.
DOI:10.1080/21655979.2022.2051786
影响因子 :4.9
-
C1R, CCL2, and TNFRSF1A Genes in Coronavirus Disease-COVID-19 Pathway Serve as Novel Molecular Biomarkers of GBM Prognosis and Immune Infiltration (2022-06-18)
期刊:DISEASE MARKERS
影响因子 :3.5
引用产品: HMC3 细胞
-
lncRNA MSC-AS1 Aggravates Diabetic Nephropathy by Regulating the miR-325/CCNG1 Axis (2022-01-25)
期刊:Journal of Healthcare Engineering
影响因子 :0.0
引用产品: 人肾小球系膜细胞完全培养基 , HMC3 细胞
-
Circ-FBXW12 aggravates the development of diabetic nephropathy by binding to miR-31-5p to induce LIN28B (2021-12-04)
期刊:Diabetology & Metabolic Syndrome
DOI:10.1186/s13098-021-00757-x
影响因子 :4.8
引用产品: HMC细胞专用培养基 , HMC3 细胞
-
Amorfrutins Relieve Neuropathic Pain through the PPARγ/CCL2 Axis in CCI Rats (2021-01-22)
期刊:PPAR Research
影响因子 :2.9
引用产品: HMC3 细胞
FAQs
Q:{{item.question}}
A:
产品资料


识别码示意图





![NCI-H82 [H82] (人小细胞肺癌细胞) (STR鉴定正确)](/Public/upfile/pic/xbx/CL-0712-1.jpg)

































