产品中心Cell Resources
联系我们CONTACT US
 400-999-210024小时服务热线
400-999-210024小时服务热线
产品概述
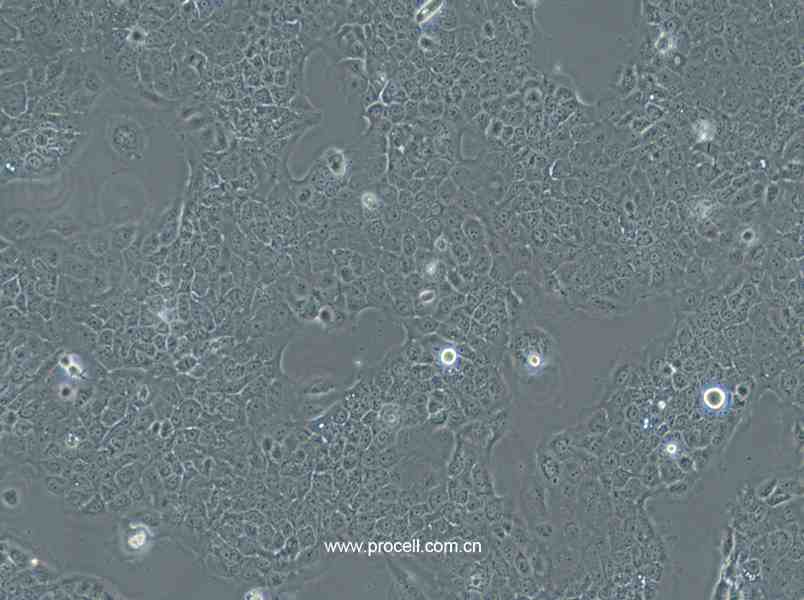
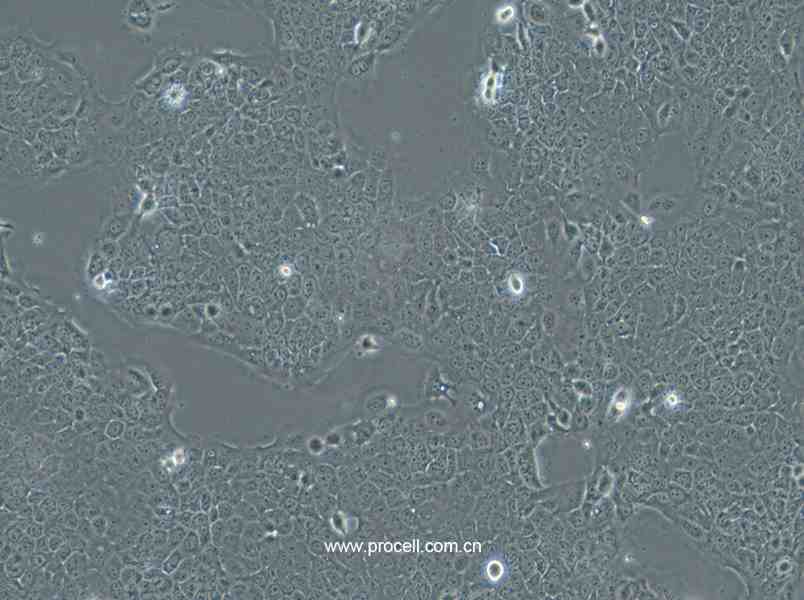
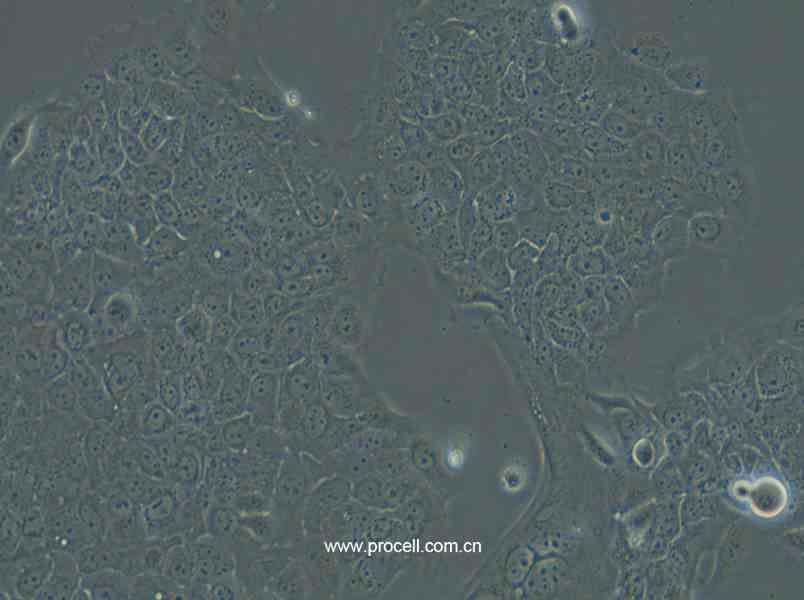
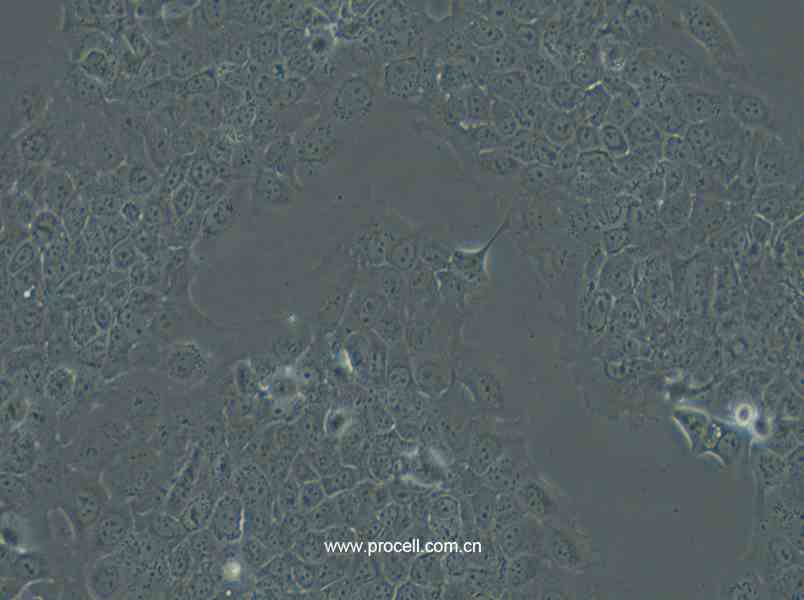
| 名称 | Ca Ski (人宫颈癌肠转移细胞/人宫颈癌上皮细胞) (STR鉴定正确) |
| 别称 | Ca-Ski; CaSki; Caski; CASKI |
| 种属 | 人 |
| 生长特性 | 贴壁细胞 |
| 细胞形态 | 上皮细胞样 |
| 冻存条件 | 冻存液:55% 基础培养基+40%FBS+5%DMSO 温度:液氮 |
| 培养方案A(默认) |
培养条件:
气相:空气,95%;CO2,5%, 温度:37℃
|
| 推荐传代比例 | 1:3-1:4 |
| 推荐换液频率 | 2-3次/周 |
| 背景描述 | Ca Ski细胞是从小肠肠系膜转移灶的细胞中建立的。据报道,Ca Ski细胞含有完整的HPV-16(每个细胞大约600个拷贝)和HPV-18相关序列。 |
| 年龄(性别) | 女性;40岁 |
| 组织来源 | 宫颈癌肠转移 |
| 细胞类型 | 肿瘤细胞 |
| 肿瘤类型 | 宫颈癌细胞 |
| 生物安全等级 | BSL-2 |
| 倍增时间 | ~60-80 hours |
| 基因表达情况 | beta subunit of human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG); tumor associated antigen |
| 保藏机构 | ATCC; CRL-1550 ATCC; CRM-CRL-1550 ATCC; CRL-7915BCRC; 60251 ECACC; 87020501 |
STR鉴定
-
STR位点信息
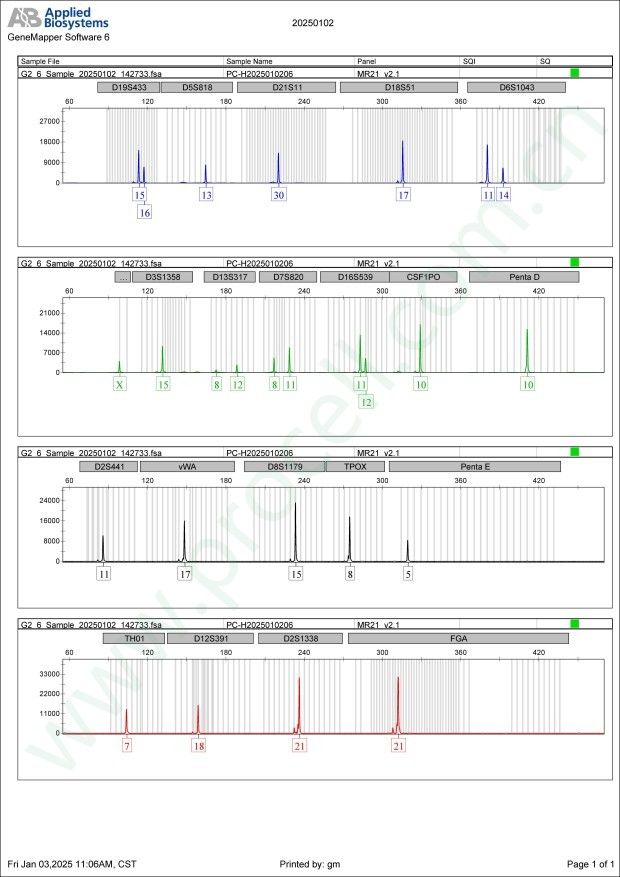
Amelogenin X CSF1PO 10 D2S1338 21 D3S1358 15 D5S818 13 D7S820 8,11 D8S1179 15 D13S317 8,12 D16S539 11,12 D18S51 17 D19S433 15,16 D21S11 30 FGA 21 PentaD 10 PentaE 5 TH01 7 TPOX 8 vWA 17 D6S1043 11,14 D12S391 18 D2S441 11 -
STR鉴定图
-
参考文献
-
NSUN7 promotes cervical cancer progression through activation of ErbB signaling pathway (2025-02-15)
期刊:FUNCTIONAL & INTEGRATIVE GENOMICS
DOI:10.1007/s10142-025-01546-9
影响因子 :3.9
-
N-acetyltransferase 10 Promotes Cervical Cancer Progression Via N4-acetylation of SLC7A5 mRNA (2025-02-20)
期刊:Frontiers in Bioscience-Landmark
影响因子 :3.3
-
SOX2 promotes the glycolysis process to accelerate cervical cancer progression by regulating the expression of HK2 (2025-01-16)
期刊:ACTA HISTOCHEMICA
DOI:10.1016/j.acthis.2025.152230
影响因子 :2.3
引用产品: Hela 细胞 , Ca Ski 细胞 , C-33 A 细胞 , SiHa 细胞 , DMEM高糖 培养基 , 特级胎牛血清 , 青霉素-链霉素溶液(双抗),100×
-
Co-freezing localized CRISPR-Cas12a system enables rapid and sensitive nucleic acid analysis (2024-10-05)
期刊:JOURNAL OF NANOBIOTECHNOLOGY
DOI:10.1186/s12951-024-02831-8
影响因子 :10.6
引用产品: Hela 细胞 , A549 [A-549] 细胞 , NCI-H292 细胞 , Ca Ski 细胞 , 16HBE 细胞
-
Function and mechanism of GBP1 in the development and progression of cervical cancer (2024-01-02)
期刊:Journal of Translational Medicine
DOI:10.1186/s12967-023-04837-6
影响因子 :7.4
引用产品: Ca Ski 细胞 , DMEM高糖 培养基
-
Combining Mitomycin C with inhibition of BAD phosphorylation enhances apoptotic cell death in advanced cervical cancer (2024-08-24)
期刊:Translational Oncology
DOI:10.1016/j.tranon.2024.102103
影响因子 :4.5
-
Oncoproteins E6 and E7 upregulate topoisomerase I to activate the cGAS-PD-L1 pathway in cervical cancer development (2024-08-02)
期刊:Frontiers in Pharmacology
DOI:10.3389/fphar.2024.1450875
影响因子 :4.4
-
HIF-1A as a prognostic biomarker related to invasion, migration and immunosuppression of cervical cancer (2024-01-13)
期刊:Heliyon
DOI:10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e24664
影响因子 :4.0
-
LIMK1 promotes the development of cervical cancer by up-regulating the ROS/Src-FAK/cofilin signaling pathway (2024-07-05)
期刊:Aging-US
影响因子 :3.9
-
APLN promotes the proliferation, migration, and glycolysis of cervical cancer through the PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway (2024-03-30)
期刊:ARCHIVES OF BIOCHEMISTRY AND BIOPHYSICS
影响因子 :3.9
引用产品: C-33 A 细胞 , Hela 细胞 , SiHa 细胞 , Ca Ski 细胞 , ECT1/E6E7 细胞 , 人子宫颈上皮细胞完全培养基
-
Serinc2 Drives the Progression of Cervical Cancer Through Regulating Myc Pathway (2024-10-17)
期刊:Cancer Medicine
影响因子 :2.9
引用产品: SiHa 细胞 , Ca Ski 细胞 , C-33 A 细胞 , 青霉素-链霉素溶液(双抗),100× , MEM 培养基
-
N6-methyladenosine methylation on FSCN1 mediated by METTL14/IGF2BP3 contributes to human papillomavirus type 16-infected cervical squamous cell carcinoma (2024-04-28)
期刊:CLINICAL AND EXPERIMENTAL PHARMACOLOGY AND PHYSIOLOGY
影响因子 :2.9
-
Study on the Role of EPHB6 in Inhibiting the Malignant Progression of Cervical Cancer C33A Cells by Binding to CBX7 (2024-09-26)
期刊:CELL BIOCHEMISTRY AND BIOPHYSICS
DOI:10.1007/s12013-024-01458-8
影响因子 :1.8
引用产品: Ca Ski 细胞
-
An anti-PD-1 antisense oligonucleotide promotes the expression of soluble PD-1 by blocking the interaction between SRSF3 and an exonic splicing enhancer of PD-1 exon 3 (2023-12-04)
期刊:INTERNATIONAL IMMUNOPHARMACOLOGY
DOI:10.1016/j.intimp.2023.111280
影响因子 :5.6
引用产品: MOLT-4 细胞 , FaDu 细胞 , Ca Ski 细胞 , HCT 116 细胞
-
PD-L1 Exon 3 Is a Hidden Switch of Its Expression and Function in Oral Cancer Cells (2023-05-03)
期刊:INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF MOLECULAR SCIENCES
影响因子 :5.6
引用产品: FaDu 细胞 , U-2 OS [U2OS] 细胞 , Ca Ski 细胞
-
IGF2BP3-mediated regulation of GLS and GLUD1 gene expression promotes treg-induced immune escape in human cervical cancer (2023-11-15)
期刊:American Journal of Cancer Research
DOI:PMID:38058838
影响因子 :5.3
-
HPV E6 promotes cell proliferation of cervical cancer cell by accelerating accumulation of RBM15 dependently of autophagy inhibition (2023-05-16)
期刊:CELL BIOLOGY INTERNATIONAL
影响因子 :3.9
引用产品: C-33 A 细胞 , Ca Ski 细胞 , SiHa 细胞 , Hela 细胞 , MEM (含NEAA) 培养基 , 特级胎牛血清 , 青霉素-链霉素溶液 (双抗),100× , RPMI-1640 培养基 , DMEM高糖 培养基 , McCoy's 5A 培养基 , DMEM/F12 培养基
-
Characterization of the microenvironment in different immune-metabolism subtypes of cervical cancer with prognostic significance (2023-02-03)
期刊:Frontiers in Genetics
DOI:10.3389/fgene.2023.1067666
影响因子 :3.7
-
Circ_0005615 promotes cervical cancer cell growth and metastasis by modulating the miR-138-5p/KDM2A axis (2023-07-02)
期刊:JOURNAL OF BIOCHEMICAL AND MOLECULAR TOXICOLOGY
影响因子 :3.6
引用产品: SiHa 细胞 , Ca Ski 细胞 , 293T [HEK-293T] 细胞 , MEM 培养基 , RPMI-1640 培养基
-
LINC00460 knockdown sensitizes cervical cancer to cisplatin by downregulating TGFBI (2023-12-28)
期刊:Chemical Biology & Drug Design
影响因子 :3.0
-
Transcription factor Dp-1 knockdown downregulates thymidine kinase 1 expression to protect against proliferation and epithelial-mesenchymal transition in cervical cancer (2023-09-16)
期刊:FUNCTIONAL & INTEGRATIVE GENOMICS
DOI:10.1007/s10142-023-01218-6
影响因子 :2.9
引用产品: C-33 A 细胞 , Ca Ski 细胞 , Hela S3 细胞 , SiHa 细胞 , 人子宫颈上皮细胞
-
Asperuloside Promotes Apoptosis of Cervical Cancer Cells through Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress-Mitochondrial Pathway (2023-04-20)
期刊:Chinese Journal of Integrative Medicine
影响因子 :2.9
-
SHCBP1 contributes to the proliferation and self?renewal of cervical cancer cells and activation of the NF?κB signaling pathway through EIF5A (2023-04-21)
期刊:Oncology Letters
影响因子 :2.9
引用产品: SiHa 细胞 , C-33 A 细胞 , Ca Ski 细胞 , DMEM/F12 培养基
-
BTG2 suppresses the growth and metastasis of cervical squamous cell carcinoma (2023-05-26)
期刊:PATHOLOGY RESEARCH AND PRACTICE
影响因子 :2.8
-
TRIM21 promotes tumor progression and cancer stemness in cervical squamous cell carcinoma (2023-07-23)
期刊:PATHOLOGY RESEARCH AND PRACTICE
影响因子 :2.8
-
Circular RNA circ_0000119 promotes cervical cancer cell growth and migration via miR-433-3p/PAK2 axis (2023-08-04)
期刊:JOURNAL OF APPLIED GENETICS
DOI:10.1007/s13353-023-00772-w
影响因子 :2.4
-
Cellular Retinoic Acid Binding Protein 2 (CRABP2), Up-regulated by HPV E6/E7, Leads to Aberrant Activation of the Integrin β1/FAK/ERK Signaling Pathway and Aggravates the Malignant Phenotypes of Cervical Cancer (2023-11-24)
期刊:BIOCHEMICAL GENETICS
DOI:10.1007/s10528-023-10568-6
影响因子 :2.4
-
PLAC8 contributes to the malignant behaviors of cervical cancer cells by activating the SOX4-mediated AKT pathway (2023-01-05)
期刊:HISTOCHEMISTRY AND CELL BIOLOGY
DOI:10.1007/s00418-022-02175-0
影响因子 :2.3
-
CircCCNB1 Knockdown Blocks the Progression of Cervical Cancer by Acting as Competing Endogenous RNA in the miR-370-3p/SOX4 Pathway (2023-01-01)
期刊:ANNALS OF CLINICAL AND LABORATORY SCIENCE
DOI:PMID:36889763
影响因子 :0.8
引用产品: MS751 细胞 , Ca Ski 细胞 , SiHa 细胞 , C-33 A 细胞 , Hela 细胞 , MEM 培养基 , RPMI-1640 培养基
-
Rapid generation of genetically engineered T cells for the treatment of virus‐related cancers (2022-09-09)
期刊:CANCER SCIENCE
影响因子 :6.5
引用产品: Ca Ski 细胞
-
CDK6 increases glycolysis and suppresses autophagy by mTORC1-HK2 pathway activation in cervical cancer cells (2022-02-15)
期刊:Cell Cycle
DOI:10.1080/15384101.2022.2039981
影响因子 :5.2
-
Signature of seven cuproptosis-related lncRNAs as a novel biomarker to predict prognosis and therapeutic response in cervical cancer (2022-09-20)
期刊:Frontiers in Genetics
影响因子 :4.8
-
OTX1 promotes tumorigenesis and progression of cervical cancer by regulating the Wnt signaling pathway (2022-09-29)
期刊:ONCOLOGY REPORTS
影响因子 :4.1
-
ZIC5 promotes aggressiveness and cancer stemness in cervical squamous cell carcinoma (2022-12-05)
期刊:PATHOLOGY RESEARCH AND PRACTICE
影响因子 :3.3
-
FBXO39 predicts poor prognosis and correlates with tumor progression in cervical squamous cell carcinoma (2022-08-28)
期刊:PATHOLOGY RESEARCH AND PRACTICE
影响因子 :3.3
-
tRNA?derived fragment tRF?Glu49 inhibits cell proliferation, migration and invasion in cervical cancer by targeting FGL1 (2022-08-09)
期刊:Oncology Letters
影响因子 :3.1
-
hsa_circ_0119412 overexpression promotes cervical cancer progression by targeting miR-217 to upregulate anterior gradient 2 (2022-03-11)
期刊:Journal Of Clinical Laboratory Analysis
影响因子 :3.1
-
Circ_0042986 Presence Restrains Cervical Cancer Development via Upregulating PEG3 by Directly Targeting miR-582-3p (2022-08-26)
期刊:Reproductive Sciences
DOI:10.1007/s43032-022-01053-3
影响因子 :2.9
引用产品: Hela 细胞 , Ca Ski 细胞 , HUVECs cell
-
Circular RNA circVPRBP serves as a microRNA-106b-5p sponge to regulate proliferation and metastasis of cervical cancer cells via tripartite motif-containing protein 3 (2022-08-10)
期刊:ANTI-CANCER DRUGS
DOI:10.1097/CAD.0000000000001335
影响因子 :2.4
引用产品: Ca Ski 细胞 , SiHa 细胞 , SiHa细胞专用培养基
-
LncRNA Opa interacting protein 5-antisense RNA 1 (OIP5-AS1) promotes the migration, invasion and epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) through targeting miR-147a/insulin-like growth factor 1 receptor (IGF1R) pathway in cervical cancer tissues and c (2022-03-01)
期刊:Journal Of Obstetrics And Gynaecology Research
影响因子 :1.6
-
Human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell-derived extracellular vesicles impede the progression of cervical cancer via the miR-144-3p/CEP55 pathway (2021-06-27)
期刊:Journal Of Cellular And Molecular Medicine
影响因子 :5.3
-
T-box transcription factor TBX1, targeted by microRNA-6727-5p, inhibits cell growth and enhances cisplatin chemosensitivity of cervical cancer cells through AKT and MAPK pathways (2021-02-08)
期刊:Bioengineered
DOI:10.1080/21655979.2021.1880732
影响因子 :4.9
引用产品: Ca Ski 细胞 , RPMI-1640 培养基 , SiHa 细胞 , MEM (含NEAA) 培养基
-
Vitamin E succinate exerts anti-tumour effects on human cervical cancer cells via the CD47-SIRPɑ pathway both in vivo and in vitro (2021-05-05)
期刊:Journal of Cancer
影响因子 :3.9
引用产品: Ca Ski 细胞
-
ASF1B promotes cervical cancer progression through stabilization of CDK9 (2020-08-26)
期刊:Cell Death & Disease
DOI:10.1038/s41419-020-02872-5
影响因子 :9.0
-
KMT2A regulates cervical cancer cell growth through targeting VDAC1. (2020-05-21)
期刊:Aging-US
影响因子 :5.2
-
Long non?coding RNA AK001903 regulates tumor progression in cervical cancer (2020-11-30)
期刊:Oncology Letters
影响因子 :2.9
-
Inhibition of miR-574-5p suppresses cell growth and metastasis and enhances chemosensitivity by targeting RNA binding protein QKI in cervical cancer cells (2019-11-30)
期刊:Naunyn-Schmiedebergs Archives of Pharmacology
DOI:10.1007/s00210-019-01772-6
影响因子 :3.6
-
MiRNA-211 triggers an autophagy-dependent apoptosis in cervical cancer cells: regulation of Bcl-2 (2019-10-21)
期刊:Naunyn-Schmiedebergs Archives of Pharmacology
DOI:10.1007/s00210-019-01720-4
影响因子 :3.6
FAQs
Q:{{item.question}}
A:
产品资料


识别码示意图